
For individuals managing diabetes, making informed dietary choices is crucial for maintaining blood sugar control and overall well-being. While certain foods can cause blood glucose spikes, others can help regulate blood sugar levels and provide essential nutrients. When it comes to navigating a diabetic-friendly diet, questions often arise about specific food items, including the humble English muffin.
The question of whether diabetics can eat English muffins is a valid one, as bread products can sometimes be tricky to incorporate into a diabetes-friendly meal plan. The answer, however, is not a simple yes or no. It depends on various factors, including the type of English muffin, portion size, and individual dietary needs.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the relationship between English muffins and diabetes, delving into their nutritional profile, impact on blood sugar levels, and how to incorporate them into a balanced diabetic diet.
Choose the Top 10 Best Bamboo Diabetic Compression Socks.
Can diabetics eat English muffins? Understanding the Role of Diet in Diabetes

i. Navigating Diabetes and Blood Sugar Control
Diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by the body’s inability to properly regulate blood sugar levels. This occurs due to either insufficient insulin production (Type 1 diabetes) or the body’s resistance to insulin (Type 2 diabetes). Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose, the primary source of energy, enter cells for utilization. When insulin function is impaired, glucose remains in the bloodstream, leading to elevated blood sugar levels and potential health complications.
ii. The Importance of Diet in Diabetes Management
Diet plays a critical role in managing diabetes, as food choices directly impact blood sugar fluctuations. A balanced diabetic diet focuses on controlling carbohydrate intake, as carbohydrates are broken down into glucose during digestion. Carefully managing carbohydrate consumption helps prevent blood sugar spikes and maintain overall glycemic control.
iii. Glycemic Index: A Guiding Tool for Diabetics
The glycemic index (GI) is a valuable tool for individuals with diabetes. It ranks carbohydrates based on their impact on blood sugar levels. Foods with a high GI cause a rapid rise in blood glucose, while low-GI foods lead to a slower and steadier increase. Diabetics are encouraged to prioritize low-GI foods to minimize blood sugar fluctuations.
iv. A Comprehensive Approach to Diabetic Meal Planning
In addition to carbohydrate management and glycemic index considerations, a healthy diabetic diet emphasizes fiber-rich foods, lean proteins, healthy fats, and an abundance of fruits and vegetables. These dietary choices promote overall well-being, weight management, and effective blood sugar control.
Understanding the principles of a diabetic diet lays the foundation for answering the question of whether individuals with diabetes can incorporate English muffins into their meal plans.
Types of Bread for Diabetics

Selecting the right types of bread can make a significant difference in managing blood sugar levels and maintaining a balanced diabetic diet. While bread is often associated with carbohydrates, which can impact blood glucose, certain varieties offer nutritional benefits and can be incorporated into a diabetic-friendly meal plan.
i. The Role of Bread in a Balanced Diabetic Diet
Bread, a staple food in many cultures, often raises concerns for individuals managing diabetes due to its carbohydrate content. However, not all bread is created equal, and certain types can be incorporated into a diabetic-friendly diet with careful consideration.
ii. Whole Grain Bread: A Nutrient-Dense Choice
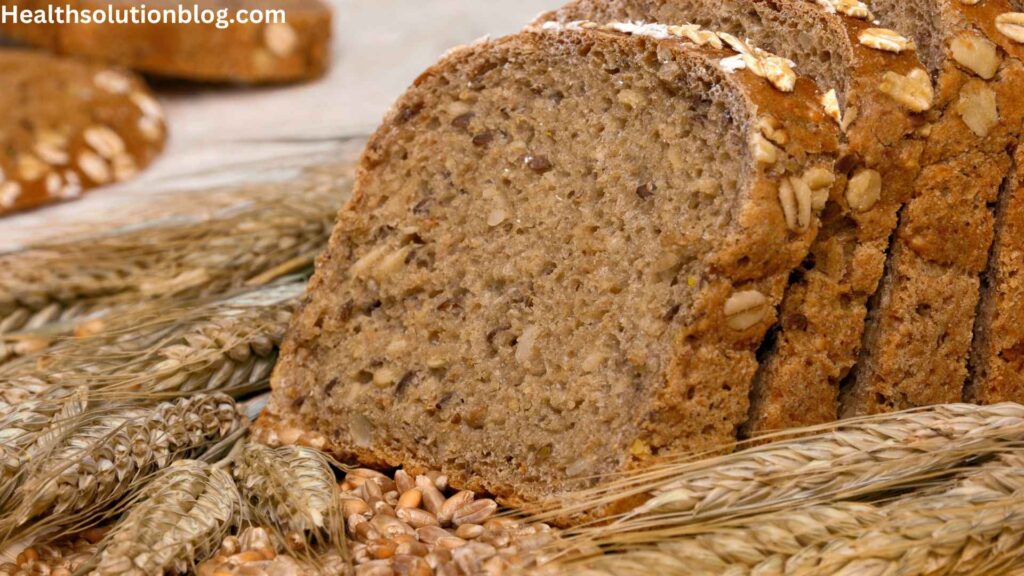

Whole grain bread is made from grains that retain all three components of the grain kernel: the bran, germ, and endosperm. This results in a bread that is rich in fiber, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. The higher fiber content in whole grain bread contributes to a lower glycemic index, making it a more suitable choice for diabetics.
iii. Whole Wheat Bread: A Fiber-rich Option
Whole wheat bread is made from whole wheat flour, which includes the entire wheat kernel, similar to whole grain bread. It is a good source of fiber, which helps regulate blood sugar levels and promotes a feeling of fullness. Whole wheat bread also provides essential nutrients like B vitamins, iron, and magnesium.
iv. Sourdough Bread: A Unique Fermentation Process
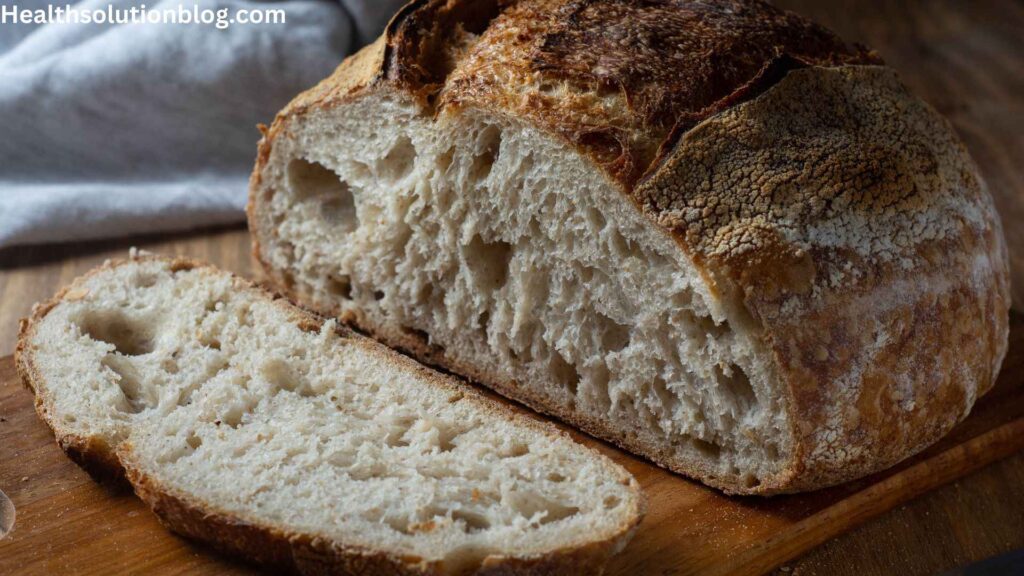

Sourdough bread undergoes a fermentation process that produces lactic acid, which can lower the glycemic index of the bread. This means that sourdough bread may have a less significant impact on blood sugar levels compared to other types of bread. Additionally, sourdough bread is often made with whole grains, further enhancing its nutritional profile.
v. Making Informed Bread Choices for Diabetes Management
When selecting bread for a diabetic-friendly diet, it is crucial to read labels carefully and choose options that are high in fiber and low in added sugars. Additionally, portion control is essential, as consuming excessive amounts of even the healthiest bread can still lead to blood sugar fluctuations.
By understanding the different types of bread and their impact on blood sugar, individuals with diabetes can make informed choices that align with their dietary goals and overall health.
vi. English Muffins: Assessing Their Suitability for Diabetics
Now, let’s turn our attention to the central question of our article: Can diabetics eat English muffins as part of their diet? To answer this question comprehensively, we’ll explore English muffins specifically and consider their place in the dietary landscape for individuals with diabetes.
English muffins, with their delightful nooks and crannies, can be an appealing choice for breakfast. However, for those with diabetes, their suitability hinges on various factors, including their nutritional content and their impact on blood sugar.
vii. Nutritional Content of English Muffins:

The nutritional profile of English muffins can vary depending on the brand and type you choose. Some factors to consider when assessing their suitability for diabetics include:
Carbohydrates: English muffins are a source of carbohydrates. It’s essential to be mindful of the total carbohydrate content, as excessive consumption can lead to blood sugar spikes.
Fiber: Look for whole grain or whole wheat English muffins with higher fiber content. Fiber can slow the absorption of glucose and promote more stable blood sugar levels.
Sugars and Sweeteners: Be aware of added sugars in some English muffin varieties. Excessive sugar can contribute to unhealthy blood sugar fluctuations.
viii. Nutritional Breakdown of English Muffins
A standard English muffin (approximately 58 grams) contains:
- Calories: 138
- Carbohydrates: 25 grams
- Fiber: 2 grams
- Protein: 5 grams
- Fat: 1 gram
While English muffins contain carbohydrates, which can impact blood sugar levels, their fiber content can help slow down the absorption of glucose, leading to a more gradual rise in blood sugar. However, it’s important to note that not all English muffins are shaped alike. Some varieties may contain added sugars, which can contribute to blood sugar spikes.
ix. Glycemic Index of English Muffins
The glycemic index (GI) of English muffins varies depending on the type of flour used. White English muffins typically have a higher GI, around 77, while whole wheat English muffins have a lower GI, around 45. This means that whole wheat English muffins are less likely to cause significant blood sugar spikes compared to white English muffins.
x. Impact on Blood Sugar Levels:
The glycemic index (GI) of English muffins can vary, but they generally have a moderate to high GI. This means they can cause a relatively rapid rise in blood sugar levels. However, the addition of fiber and the specific type of English muffin (e.g., whole grain or sourdough) can influence this effect.
xi. Incorporating English Muffins into a Balanced Diabetic Diet
English muffins can be part of a balanced diabetic diet when consumed in moderation and paired with protein-rich and fiber-rich toppings. For instance, topping an English muffin with scrambled eggs, avocado, or nut butter can help balance the carbohydrate content and promote a slower release of glucose into the bloodstream.
Ultimately, the decision of whether to include English muffins in a diabetic diet should be made in consultation with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian, considering individual dietary needs and blood sugar management goals.
Portion Control and Frequency

As we navigate through the landscape of incorporating English muffins into the diets of individuals with diabetes, it’s essential to understand that both portion control and frequency play critical roles in maintaining stable blood sugar levels.
i. Importance of Portion Control:
For diabetics, portion control is not just a suggestion; it’s a vital practice. English muffins, like many other foods, can be a part of a balanced diet when consumed in the right amounts. Keeping portion sizes in check helps prevent excessive carbohydrate intake, which can lead to unwanted spikes in blood sugar.
ii. How Often Can Diabetics Consume English Muffins?

The frequency of English muffin consumption for individuals with diabetes varies from person to person. It’s influenced by factors like overall dietary habits, physical activity, and blood sugar management goals. Some key considerations include:
Meal Planning: When incorporating English muffins, it’s crucial to plan meals that balance carbohydrates, proteins, and healthy fats. This can help distribute glucose intake more evenly throughout the day.
Occasional Treat: For some, English muffins can be an occasional treat, enjoyed sparingly. This approach can help avoid frequent blood sugar fluctuations.
Glycemic Load: Monitoring the glycemic load of the meal is essential. Combining an English muffin with foods that have a lower glycemic index can help mitigate its impact on blood sugar levels.
Personalized Guidance: Working with a healthcare professional, such as a dietitian or endocrinologist, can provide personalized advice on the frequency and portion sizes that suit an individual’s unique needs.
iii. Navigating Breakfast Options for Diabetics: English Muffins and Beyond
While English muffins can be part of a balanced diabetic breakfast, it’s essential to consider other nutrient-rich options that can provide a variety of health benefits. Here’s a comparison of English muffins with other diabetic-friendly breakfast choices:
Oatmeal:
- Pros: Oatmeal is a whole-grain cereal that is high in fiber, which helps regulate blood sugar levels and promotes satiety. It also contains essential nutrients like magnesium, potassium, and B vitamins.
- Cons: Some varieties of instant oatmeal may contain added sugars, so it’s important to choose plain oatmeal and add natural sweeteners like fruit or honey in moderation.
Eggs:
- Pros: Eggs are a rich source of protein, which helps slow down the absorption of carbohydrates and stabilize blood sugar levels. They also contain essential nutrients like choline, vitamin D, and B vitamins.
- Cons: Eggs are relatively high in cholesterol, so individuals with specific dietary restrictions or health concerns should consult their healthcare provider for personalized recommendations.
Greek Yogurt:
- Pros: Greek yogurt is a high-protein, low-sugar option that provides probiotics, and beneficial bacteria that support gut health. It is also a good source of calcium and vitamin D.
- Cons: Some flavored Greek yogurts may contain added sugars, so it’s important to choose plain Greek yogurt and add toppings like berries or nuts for sweetness and texture.
iv. Additional Diabetic-Friendly Breakfast Choices:
- Avocado toast: Whole-grain toast topped with avocado provides fiber, healthy fats, and essential nutrients.
- Nut butter and fruit: A combination of nut butter and fruit on whole-grain bread or crackers offers a balance of protein, fiber, and natural sugars.
- Cottage cheese with berries: Cottage cheese is a protein-rich option that can be paired with berries for added fiber and antioxidants.
v. Considering Individual Needs and Preferences
The ideal breakfast choice for individuals with diabetes depends on personal preferences, dietary restrictions, and blood sugar management goals. It’s important to consider the overall nutritional profile of each option and how it fits into a balanced meal plan.
Regularly monitoring blood sugar levels after consuming different breakfast foods can help individuals identify which options work best for their individual needs and glycemic control. Consulting with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian can provide personalized guidance on meal planning and food choices to optimize diabetes management and overall health.
English Muffin Varieties

As we explore whether diabetics can include English muffins in their diet, it’s essential to consider the diverse range of English muffin varieties available. Two notable options for individuals with diabetes are whole grain and sourdough English muffins.
i. Whole Grain English Muffins:
Impact on Blood Sugar and Health:
Whole-grain English muffins, rich in fiber, offer a potential advantage for blood sugar management due to their slower glucose absorption.
The higher fiber content not only aids in blood sugar control but also supports overall health by promoting better digestion and heart health.
Opting for whole-grain English muffins can be a wise choice for diabetics who wish to enjoy this classic breakfast item while keeping their blood sugar in check.
ii. Sourdough English Muffins (Alternative):
Impact on Blood Sugar and Health:
Sourdough English muffins, thanks to their fermentation process, may have a lower glycemic index (GI) compared to traditional white bread products.
A lower GI suggests that sourdough English muffins might have a more gradual effect on blood sugar levels, making them an intriguing alternative for diabetics.
Although more research is needed, sourdough English muffins provide an appealing choice for individuals seeking to manage blood sugar.
Cooking Tips and Toppings
In this section, we’ll provide practical advice on how to make English muffins a healthier choice for diabetics and suggest diabetic-friendly toppings.
i. Cooking Tips for Diabetics:

Lightly toasting English muffins can enhance their flavor without adding extra sugar or fat.
Opt for whole grain or whole wheat English muffins for higher fiber content and a slower impact on blood sugar levels.
Consider a thin spread of heart-healthy fats, like avocado or a small amount of nut butter, instead of butter or sugary spreads.
ii. Diabetic-Friendly Toppings:
Peanut Butter: Choose natural, unsweetened peanut butter for a protein-rich topping that adds a creamy, nutty flavor.
Almond Butter: Similarly, almond butter provides a different flavor profile and is packed with protein and healthy fats.
Avocado: Mashed avocado is a nutrient-rich and creamy topping that’s also an excellent source of healthy fats.
iii. Navigating a Balanced Diet for Diabetes Management:
A well-rounded and balanced diet is essential for individuals with diabetes to effectively manage blood sugar levels, maintain a healthy weight, and promote overall well-being. While specific dietary recommendations may vary based on individual needs and health goals, some general principles apply:
iv. Prioritize Nutrient-Dense Whole Foods:
- Focus on consuming whole, unprocessed foods that are naturally rich in nutrients and fiber.
- Include plenty of fruits and vegetables, opting for a variety of colors and types to maximize nutrient intake.
- Choose whole grains over refined grains, such as whole wheat bread, brown rice, and quinoa.
- Incorporate lean protein sources, such as fish, poultry, beans, and lentils, into your meals.
v. Limit Processed Foods and Added Sugars:
- Minimize consumption of processed foods, which often contain high amounts of added sugars, unhealthy fats, and sodium.
- Read food labels carefully and choose products with lower sugar content or opt for naturally sweetened alternatives.
- Avoid sugary drinks, including sodas, juices, and sweetened coffee or tea. Instead, opt for water, unsweetened tea, or sparkling water with a squeeze of citrus.
vi. Practice Portion Control and Regular Meal Timing:
- Divide your daily food intake into regular meals and snacks to maintain stable blood sugar levels and prevent overeating.
- Use visual cues, such as measuring portions or comparing food portions to familiar objects, to aid in portion control.
- Avoid skipping meals, as this can lead to fluctuations in blood sugar and increased cravings for unhealthy snacks.
vii. Seek Guidance from Healthcare Professionals:
- Consulting with a healthcare provider or registered dietitian can provide personalized meal-planning advice tailored to your specific needs and health goals.
- A healthcare professional can help you create a balanced meal plan that considers your individual preferences, dietary restrictions, and blood sugar management targets.
- Regular follow-up appointments can ensure your meal plan is adjusted as needed based on changes in your health status or medication regimen.
Remember, a balanced diet is not about deprivation but about making informed choices that support your overall health and well-being. By incorporating nutrient-dense foods, practicing portion control, and seeking guidance from healthcare professionals, individuals with diabetes can effectively manage their blood sugar levels and enjoy a fulfilling and enjoyable eating pattern.
Expert Opinions
i. Registered Dietitian:
“English muffins can be part of a healthy diabetic diet when consumed in moderation and paired with protein-rich and fiber-rich toppings. Whole wheat or sourdough English muffins are preferred choices due to their lower glycemic index and higher fiber content. However, portion control is essential, and individuals should limit consumption to one-half or one whole English muffin per meal.”
ii. Nutritionist:
“When choosing English muffins for a diabetic-friendly meal, it’s crucial to read labels carefully and opt for varieties with minimal added sugars and sodium. Additionally, consider toasting English muffins to slightly lower their glycemic index and enhance their texture.”
iii. Additional Expert Tips:
- Pair English muffins with fiber-rich toppings like avocado, beans, or chia seeds to slow down carbohydrate absorption and promote a more gradual rise in blood sugar levels.
- Incorporate protein-rich toppings like eggs, lean meats, or Greek yogurt to balance the carbohydrate content and promote satiety.
- Avoid sugary toppings like jams, jellies, or syrups, which can cause blood sugar spikes.
- Experiment with different flavor combinations to find options that are both nutritious and enjoyable.
- Consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian for personalized guidance on incorporating English muffins and other foods into a diabetic meal plan.
Remember, individual responses to food can vary, and it’s essential to monitor blood sugar levels after consuming English muffins to determine their impact on your blood glucose control. By making informed choices, practicing portion control, and seeking personalized guidance from healthcare professionals, individuals with diabetes can enjoy English muffins as part of a balanced and healthy diet.
Conclusion
As we conclude this comprehensive guide on English muffins and their role in a diabetic-friendly diet, we invite you to revisit the wealth of information provided throughout this article. From understanding the glycemic index to exploring expert opinions, you’ve gained valuable insights into making informed choices about incorporating English muffins into your meal plan.
Remember, the key to enjoying English muffins while managing diabetes lies in mindful consumption, informed choices, and personalized guidance from healthcare professionals. By embracing these principles, you can navigate your dietary decisions with confidence and savor the flavors and versatility of English muffins without compromising your blood sugar control.
Now, we invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with English muffins as a diabetic. What strategies have you found helpful in incorporating them into your diet? What are your favorite diabetic-friendly toppings or recipes? Your insights and experiences can enrich the conversation and empower others on their journey of managing diabetes and enjoying a fulfilling, nourishing lifestyle.
FAQs: Can diabetics eat English muffins?
Can diabetics eat English muffins?
Yes, diabetics can consume English muffins in moderation as part of a balanced diet. However, it’s crucial to choose whole wheat or sourdough varieties, practice portion control, and pair them with protein-rich and fiber-rich toppings.
What type of English muffin is best for diabetics?
Whole wheat or sourdough English muffins are preferred choices due to their lower glycemic index and higher fiber content. These varieties can help manage blood sugar levels more effectively.
How many English muffins can a diabetic eat per day?
Limit consumption to one-half or one whole English muffin per meal. Monitor blood sugar levels after eating to determine individual tolerance.
What are some diabetic-friendly toppings for English muffins?
Pair English muffins with protein-rich toppings like eggs, lean meats, or Greek yogurt, and fiber-rich toppings like avocado, beans, or chia seeds. Avoid sugary toppings like jams, jellies, or syrups.
Does toasting English muffins affect their glycemic index?
Yes, toasting English muffins can slightly lower their glycemic index, making them a better choice for diabetics. Toasting also enhances their texture.
What are some other diabetic-friendly breakfast options?
Oatmeal, eggs, Greek yogurt, avocado toast, nut butter and fruit, and cottage cheese with berries are all suitable breakfast choices for diabetics.
How can I manage my blood sugar levels effectively as a diabetic?
Adopt a balanced diet rich in whole grains, fiber, protein, and healthy fats. Practice portion control, regular meal timing, and physical activity. Consult a healthcare professional for personalized guidance.
What resources are available for diabetics to learn more about diet and blood sugar management?
Reliable online resources include the American Diabetes Association, Diabetes Canada, and the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Consult a registered dietitian or certified diabetes educator for personalized meal planning and support.
What should I do if I experience blood sugar fluctuations after eating English muffins?
Monitor blood sugar levels regularly and discuss any concerns with your healthcare provider. They can help adjust your meal plan or medication regimen as needed.
How can I incorporate English muffins into my diabetic meal plan without compromising my health goals?
Choose whole wheat or sourdough varieties, limit portion size, pair with protein-rich and fiber-rich toppings, and consult a healthcare professional for personalized guidance.
Sources:
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/317067#eggs
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7231599/
https://www.webmd.com/diabetes/ss/slideshow-breakfast-ideas-diabetes


