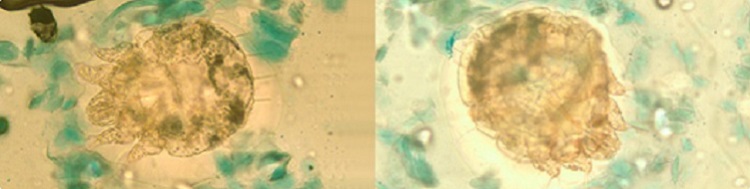
Scabies is an extremely contagious disease that is caused by a tiny eight-legged mite called Sarcoptes scabiei var. hominis which burrows in the skin. The direct answer to the question is, that it looks like red, pimple-like bumps, thin, wavy lines under the skin (burrows), and crusty sores which are accompanied by intense itching, especially at night.
For more details of scabies and understanding their symptoms, and their appearance, this article dwells into the characteristics of scabies, their early signs, the importance of quick identification, and why seek professional help.
2. Characteristics of Scabies Rash
Scabies is an itchy rash that often takes a characteristic pattern. Following are the hallmarks of scabies:
2.1 Red, pimple-like bumps:
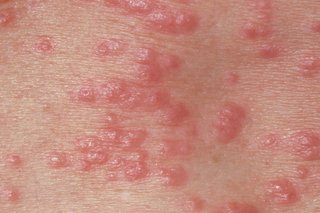
Red, pimple-like bumps on the skin are the first noticeable hallmark of scabies. These bumps are the initial clue signaling the presence of mites under the skin. Keen observation is crucial for detecting this condition in the early stage.
2.2 Intense Itching:
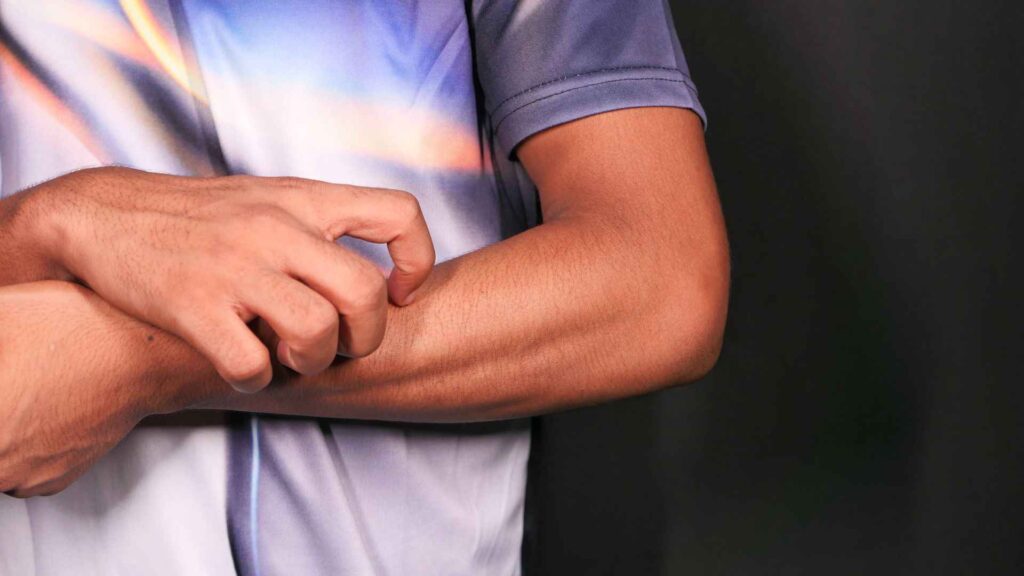

This is the most notorious and persistent symptom of scabies which can be ruthless, particularly at night. Upon scratching it urge to scratch more and can lead to secondary infections.
2.3 Burrows:
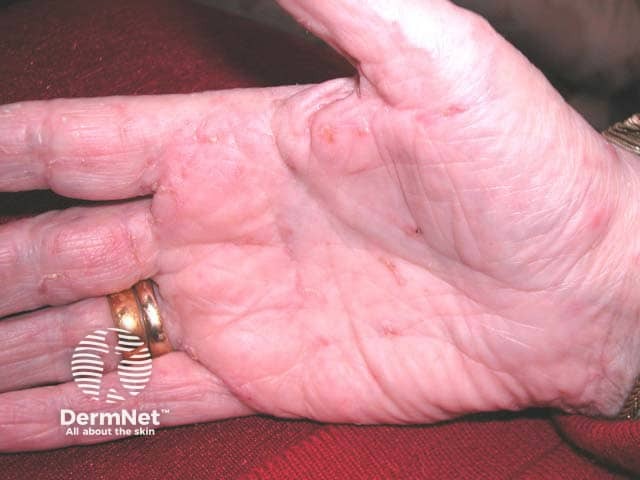
This is the real and unique symptom of scabies. While scabies may be microscopic but the trails they leave are distinctly visible. These burrows are tiny tunnels that are created by female mites when they are laying eggs while burrowing under the skin.
2.4 Crusty Sores:
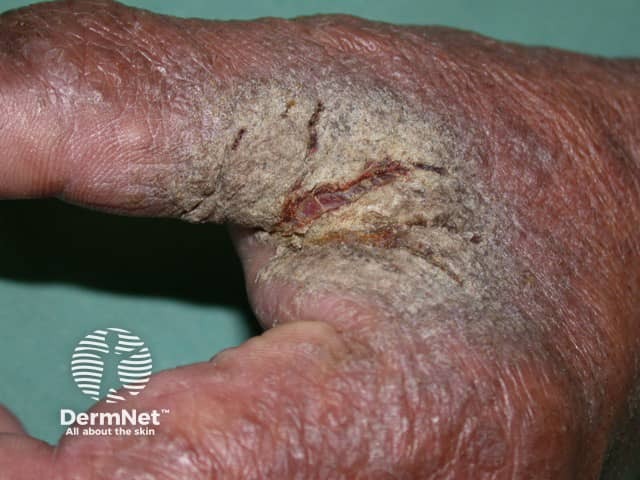
In severe cases, especially in infants and people with weakened immune systems, scabies can cause thick crusty sores.
3. Distribution Patterns on the Skin:
Scabies can affect any part of the body but the most common areas are:
3.1 Common Areas Affected:
- Webbed spaces between fingers: Due to a moist, warm environment this area is the prime target for scabies mites. Look for any blisters or bumps in these areas.
- Wrists and inner elbows: Wrists and elbows (both inner and outer) are another convenient site for mites to infect. Watch out for any signs of scabies in these areas.
- Armpits and waistline: Armpits and waistline with belly buttons are another favorite site of scabies. Watch out for signs of intense itching for early detection.
- Buttocks and genital area: When scabies advance it also affects these sensitive areas where they appear as tiny bumps, blisters, or even burrow tracks.
- Soles of the feet: In babies and children scabies appear on the soles of feet as red bumps, blisters, and itching.
- Face and scalp: These are also common areas in infants and children where scabies manifest as blisters and crusting on the face and scalp.
Remember, these are general patterns. If you notice any bumps or blisters with intense itching, it is better to consult with a doctor for a proper diagnosis. But by understanding the appearance and distribution of scabies you may avoid the worse condition by treating them in the early stage.
4. Identifying Burrows on Different Skin Types:
Scabies infect all skin tones but the appearance and detection may vary.
4.1 Manifestations on Lighter Skin Tones:
The sign is clearly visible on lighter skin tones where it appears as visible red bumps and clear burrows.
4.2 Manifestations on Darker Skin Tones:
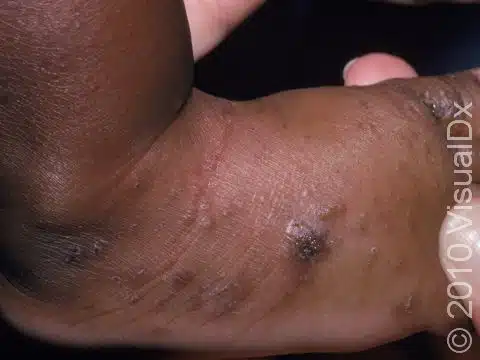
The manifestation on darker skin is a bit challenging because the signs like redness and inflammation are masked by darker tones. While the challenge may hurdle the diagnosis but remember, that the itching is the key indicator for scabies which needs to be checked by a doctor.
5. How to distinguish scabies signs from other skin conditions:
While the scabies burrows are unique but they may be mistaken for other skin diseases. Here is a table for comparison:
| Skin Condition | Appearance | Location | Itching |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scabies Burrows | Thin, wavy, grayish-white or skin-colored lines | Webbed spaces between fingers, wrists, elbows, armpits, waistline, buttocks, and genitals | Intense, especially at night |
| Eczema | Red, scaly patches, often with blisters | Anywhere on the body | Itchy, but usually not as intense as scabies |
| Dermatitis | Red, inflamed patches with oozing or crusting | Arms, legs, face | Varies depending on type of dermatitis |
| Insect bites | Small, red, itchy bumps | Anywhere on the body | Usually fades within a few days |
6. Scabies Impact on Sensitive and other Skin’s conditions skin:
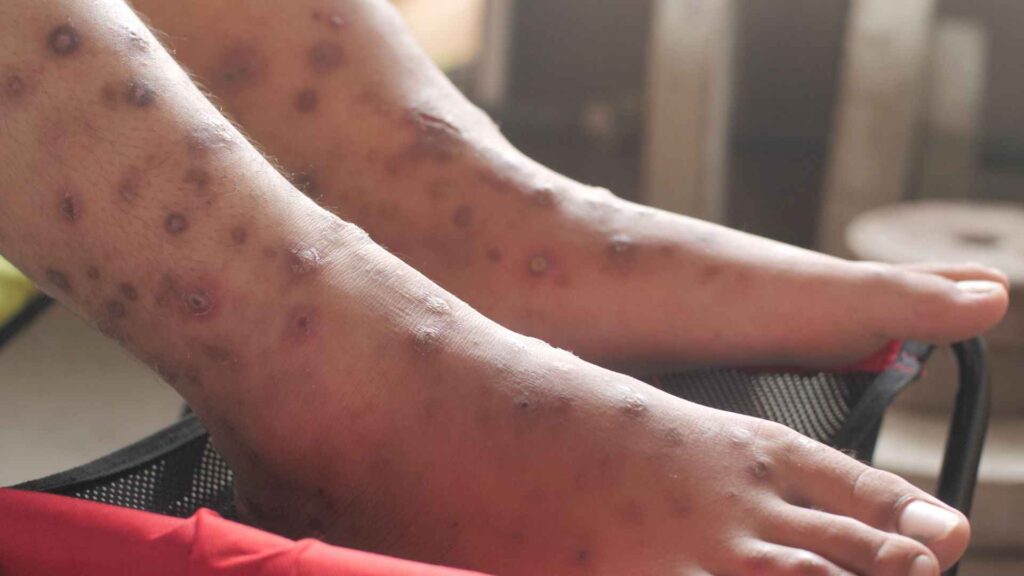
For those with sensitive skin and other conditions like dermatitis or eczema, scabies can be a double whammy. The burrowing mites with intense itching can lead to allergic reactions which may:
- Increased inflammation and redness: The sensitive skin reacts more intensely to scabies which results in amplified redness, swelling, and irritation.
- Intensified itching and discomfort: Intensified itching when accompanied by sensitive skin and other skin conditions like eczema and dermatitis can lead to scratching-induced wounds.
- Slower healing: The constant scratching and inflammation can break the scabies lesion which prolongs the healing process.
6.1 Special considerations for sensitive skin:
- Gentle touch: when dealing with scaies on sensitive skin, opt for gentle, fragrance-free cleansers and moisturizers, and hypoallergenic products. Harsh scrubbing can exaggerate the scabies.
- Targeted treatment: Consult with a dermatologist who recommends a treatment plan according to your sensitive skin condition and any other co-existing disease like eczema or dermatitis.
- Extra vigilance: Monitor your treatment and any progress in scabies, and report any worsening symptoms to your doctor, if happen.
7. Seeking Professional Help:
While the signs and symptoms are identified by you, treating this itchy condition requires the expertise of a healthcare professional. The early detection of signs and symptoms can help to save you from worse conditions while seeking professional help can ensure the appropriate treatment, and prevent its spread to others.
7.1 Why Consulting a Doctor Matters:
The main benefit of consulting a doctor is:
7.1.1 Diagnostic Tests for Confirmation:
While the expertise knowledge and visual examination of a doctor are obvious but simple tests like skin scraping or KOH (potassium hydroxide) testing confirm the presence of scabies mites or their eggs which is done by your doctor.
In this test, the skin scraping is taken and put on a slide with KOH solution on it. The KOH dissolves the skin cells and leaves scabies, their eggs, fungi, or fecal material making it easy to identify under a microscope.
7.2 Treatment Options and Considerations:
After diagnosis, the doctor will adopt a treatment plan specifically for your needs. This involves prescription medications and preventive measures for reinfection:
7.2.1 Prescription Medications:
- Topical creams and lotions: Scabicides like permethrin or crotamiton which are directly applied on infected areas to kill the mites and their eggs.
- Oral medications: In severe cases for infants and pregnant women where topical application might be a problem or not so effective, an oral medication like ivermectin might be prescribed to kill the scabies mites internally.
Some Additional Tips:
- Inquire and ask about the potential side effects of the prescribed medications from your doctor.
- Discuss any underlying skin problems or allergies with your doctor before starting the treatment plan.
- Ask and clarify any doubts about the treatment plan.
8. Preventive Measures and Hygiene Practices:
As discussed at the start, scabies is a highly contagious disease that must be prevented from spreading. Some preventive measures are:
- Separate all beddings, clothing, Bathing Products, and Towels: First and foremost, it is crucial to separate all beddings, clothing, bathing products towels, and sharing personal items from others.
- Washing all bedding, clothes, and towels: Use hot water and laundry detergent to kill any remaining mites.
- Keep all beddings, clothing, and Towels in the sun: If washing is not possible or even after washing, keep all the beddings, clothing, and towels in the sun all day to kill scabies mites.
- Treating close contacts: Close contacts should also visit the doctor even if they have no symptoms as the mite may divide in the skin in its initial stages. Early detection can stop the spread of the disease.
- Avoiding scratching: Try to avoid scratching because scratching can worsen the condition and can spread the mites to other areas of the body.
Following your doctor’s instructions and completing the entire treatment plan can eradicate the culprit and prevent it from re-infection.
Additional Tips:
- Trim your nails to prevent scratching which could lead to a wound and worsen the condition.
- Avoid using harsh soaps and scrubs that can further irritate the skin.
- Stay cool and avoid overheating because sweating can worsen the itch.
- Maintain good hygiene to cut the risk of secondary infections.
9. Home Remedies and Care for Scabies
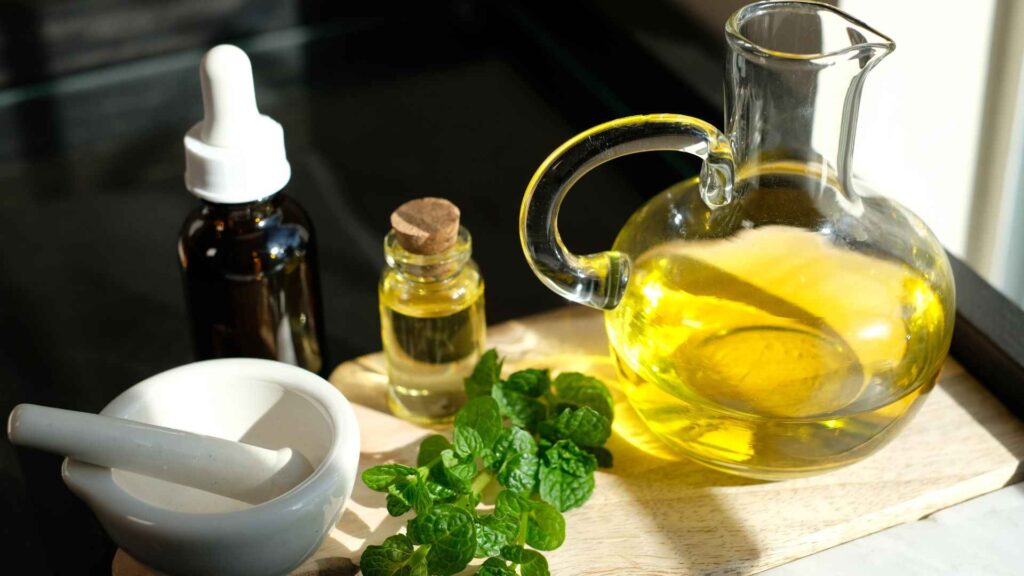

Though scabies require professional treatment, certain home remedies and care can offer comfortable relief and prevent their spread. Here are some recommendations:
9.1 Soothing the Itching Sensation:
The scabies can be relieved by going with the following options.
9.1.1 Over-the-counter Creams and Lotions:
- Calamine lotion: This lotion can offer temporary relief from itching and mild inflammation.
- Anti-itch creams: Look for creams and lotions that contain diphenhydramine or pramoxine to offer topical itch relief.
9.1.2 Natural Remedies and Their Efficacy
While the importance of professional treatment is in its place but natural remedies can also provide relief from scabies perfectly.
Ingredients like tea tree oil, neem oil, and aloe Vera are known for their soothing and antimicrobial properties.
Colloidal oatmeal is known for its anti-inflammatory properties that can help to soothe irritation and itching. It can be used when soaked in lukewarm water for 15-20 minutes.
Aloe Vera can be directly applied to infected areas for a cooling and soothing effect.
Conclusion/Summary:
Scabies is a highly contagious disease that is caused by a tiny mite called Sarcoptes scabiei that individuals must recognize in the early stage for effective treatment and management. It usually appears as red, pimple-like bumps, thin, wavy burrows, or crusty sores in severe conditions with intense itching especially at night time.
Sensitive skin and individuals with already skin diseases like eczema and dermatitis face the extra challenge of heightened discomfort.
To prevent worse conditions professional healthcare especially dermatologist consultation becomes crucial as the expertise knowledge with diagnostic tests the dermatologist can identify the condition accurately and prescribe medications and instructions to eradicate it.
Over-the-counter medications and home remedies like tea tree oil, neem oil, and aloe vera can be a soothing solution for this condition.
Have you experienced symptoms of scabies? Share your story and tips in the comments below.
FAQs- what does scabies look like on the skin
What does scabies look like on the skin?
Scabies look like red pimple-like bumps and thin, wavy lines and crusty sores which are accompanied by intense itching, especially at night.
How can I recognize scabies symptoms early?
Itching is the notorious symptom of scabies which is coupled with signs like red bumps, inflammation, and the appearance of burrows on the skin. Immediate medical help is crucial.
Can scabies affect different skin types differently?
Yes, scabies can affect individuals with sensitive skin differently where it heightens the discomfort and allergic reactions. Detection on darker skin tones might be a challenge.
Why is consulting a healthcare professional important for scabies?
Healthcare professionals may conduct confirmation tests for scabies which surely identify the mites in the skin. Also, the expertise knowledge helps to diagnose the condition accurately and design an effective treatment plan and preventive measures.
What is the one common sign of scabies that can help to identify in darker skin easily?
If the detection in darker tones is a challenge, which can be solved by examining in well-lit areas or using a dermascope, remember, that itching is a common cause for scabies which can help to identify in all skin types and tones.
Are there home remedies for managing scabies symptoms?
Yes, over-the-counter creams like Calamine lotion and creams with diphenhydramine or pramoxine, natural remedies like tea tree oil, neem oil, and aloe vera, and thorough cleaning measures can help to soothe the itch and prevent it from spreading within the household.
How can scabies spread be prevented at home?
Preventing measures include isolation, hot water laundering, drying the laundry in the hot sun, and cleaning can minimize the spread at home.
Sources:
https://www.cdc.gov/parasites/scabies/index.html





