
Melanin, the pigment that gives our skin its color, plays a dual role in our lives: it’s a guardian of skin health and a factor in aesthetic preferences. As a natural shield, melanin absorbs the sun’s harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays, preventing them from penetrating deeper skin layers and protecting us from sunburn, premature aging, and even skin cancer. However, melanin’s role in skin pigmentation also leads to concerns about aesthetic ideals, with lighter skin tones often being associated with beauty standards in some cultures.
Understanding the science behind melanin production and exploring natural ways to enhance melanin levels without compromising skin health is crucial for making informed decisions about our skin. By striking a balance between skin health and aesthetic preferences, we can embrace our unique skin tones while safeguarding our skin from the sun’s harmful effects.
In this article, we’ll delve into the fascinating world of melanin, exploring its role in both skin health and beauty perception. We’ll uncover the science behind melanin production and discover 10 delectable and nutrient-rich foods that can naturally boost melanin levels, promoting radiant skin without compromising your well-being.
2. Digging into the Science of Melanin Production
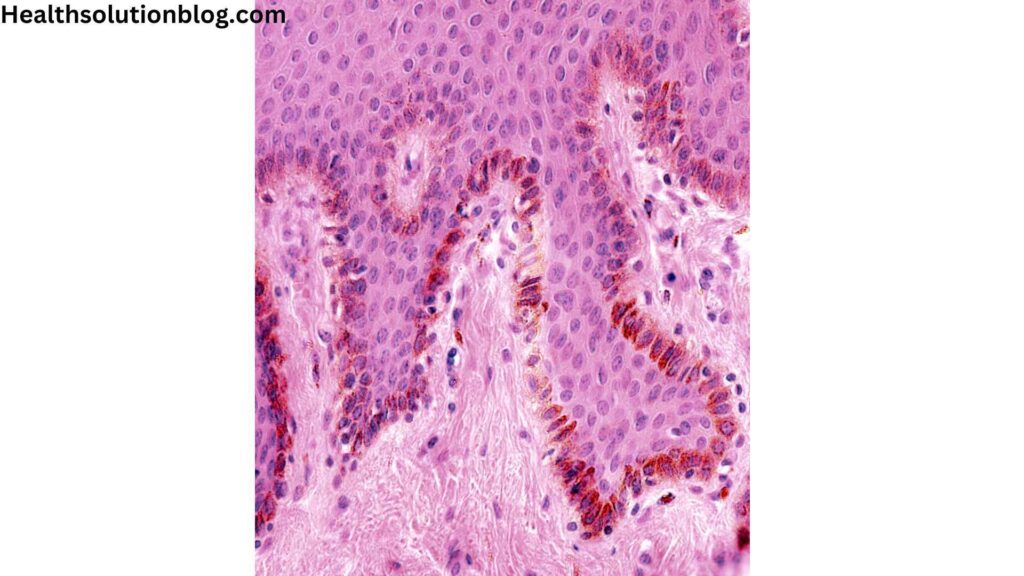
2.1. Understanding the Role of Melanocytes and Tyrosinase
The journey of melanin production begins within specialized cells called melanocytes, which reside in the deepest layer of the epidermis, the outer skin layer.
These melanocytes are equipped with tyrosinase, an enzyme that plays a pivotal role in melanin synthesis.
Tyrosinase acts as a catalyst, initiating a series of chemical reactions that transform the amino acid tyrosine into melanin.
This complex process involves oxidation and polymerization, resulting in the formation of melanin pigments.
2.2. Exploring the Factors Affecting Melanin Production
Melanin production is influenced by a multitude of factors, both internal and external.
Genetics plays a significant role in determining the inherited amounts of melanocytes and tyrosinase activity.
Hormones, particularly melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH), also exert a strong influence on melanin production, stimulating the melanocytes to produce more melanin.
External factors, such as sun exposure, can also trigger an increase in melanin production.
When UV rays penetrate the skin, they activate melanocytes, leading to enhanced tyrosinase activity and melanin synthesis.
This natural defense mechanism helps protect the skin from the damaging effects of UV radiation.
2.3. Unraveling the Process of Melanin Distribution
Once melanin is produced within melanocytes, it is packaged into specialized organelles called melanosomes.
These melanosomes act as tiny transporters, carrying the melanin pigments to the surrounding keratinocytes, the cells that make up the bulk of the epidermis.
Melanosomes are then transferred to the outermost layer of the epidermis, where they distribute themselves evenly, creating a protective shield against UV radiation.
This distribution process ensures that all skin cells are equipped with melanin, providing a uniform defense against the sun’s harmful rays.
3. Enhancing Melanin Production Naturally: Dietary Pillars

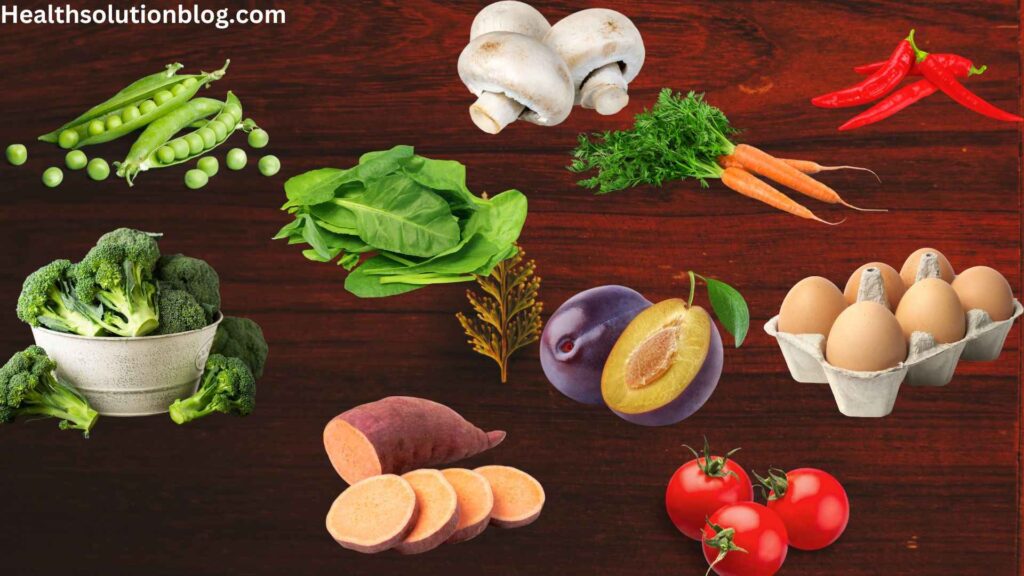
3.1. Fruits, Vegetables, and Whole Grains: A Masterpiece of Nutrients
Nature’s abundance offers an abundance of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains that provide a rich source of nutrients essential for melanin production.
These dietary pillars supply the building blocks for melanin synthesis, including amino acids, vitamins, and minerals.
A diet rich in fruits and vegetables, particularly those with vibrant colors, is key to enhancing melanin production.
These plant-based foods are packed with antioxidants, which protect melanocytes from damage and promote their overall health.
Whole grains, such as brown rice, quinoa, and oats, contribute to a balanced diet and provide essential nutrients for melanin synthesis.
3.2. Harnessing the Power of Beta-Carotene and Vitamin A
Beta-carotene, a precursor to vitamin A, plays a crucial role in melanin production.
When consumed, beta-carotene is converted into vitamin A, which stimulates melanocyte activity and enhances melanin synthesis. Foods rich in beta-carotene include carrots, sweet potatoes, spinach, and kale.
Vitamin A, in both its preformed and precursor forms, is essential for maintaining healthy skin and supporting melanin production.
It promotes cell growth and differentiation, ensuring the proper function of melanocytes. Vitamin A-rich foods include liver, eggs, and dairy products.
3.3. Vitamin C: A Potential Melanin Enhancer
Vitamin C, a potent antioxidant, is believed to play a role in enhancing melanin production.
While research is still ongoing, evidence suggests that vitamin C may protect melanocytes from oxidative stress and promote tyrosinase activity.
Foods rich in vitamin C include citrus fruits, strawberries, bell peppers, and broccoli. Incorporating these vitamin C-rich foods into one’s diet may contribute to overall skin health and potentially enhance melanin production.
3.4. Antioxidants: Beyond Melanin Enhancement
Antioxidants, found abundantly in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, play a broader role in skin health beyond melanin enhancement.
These powerful molecules combat free radicals, unstable molecules that can damage skin cells and accelerate aging. By neutralizing free radicals, antioxidants protect melanocytes and promote overall skin health.
A diet rich in antioxidants not only supports melanin production but also contributes to a radiant, youthful complexion.
4. Lifestyle Practices for Melanin Support

4.1. Sun Exposure: Striking a Balance
While sun exposure is essential for vitamin D synthesis and can trigger melanin production, excessive sun exposure can lead to sunburn and increase the risk of skin cancer.
It’s crucial to strike a balance between sun exposure and sun protection.
Moderate sun exposure, particularly during the early morning hours, can stimulate melanin production without causing harm.
However, excessive sun exposure, especially during midday hours, should be avoided. Seek shade during peak sun hours, and wear protective clothing and sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30 when venturing outdoors.
4.2. Herbs and Spices: Nature’s Melanin Allies
Certain herbs and spices may offer potential benefits for melanin production.
Turmeric, with its curcumin content, has been shown to protect melanocytes from oxidative stress. Licorice root extract may also play a role in melanin enhancement.
While more research is needed to fully understand the effects of herbs and spices on melanin production, incorporating them into one’s diet may provide additional support for skin health.
Consult with a healthcare professional or herbalist for guidance on specific herbs and their appropriate use.
4.3. Exercise and Overall Health: A Synergistic Approach
Maintaining overall health through regular exercise, a balanced diet, and adequate sleep can contribute to healthy skin and potentially support melanin production.
Exercise promotes blood circulation, delivering essential nutrients to melanocytes, while a balanced diet provides the building blocks for melanin synthesis.
Adequate sleep is also crucial for skin health, allowing the body to repair and regenerate cells, including melanocytes.
Aim for 7-8 hours of quality sleep each night to support your skin’s overall health and potentially enhance melanin production.
Remember, these lifestyle practices should be considered in conjunction with a balanced diet that includes foods rich in melanin-boosting nutrients.
5. 10 Melanin-Boosting Foods for Radiant Skin
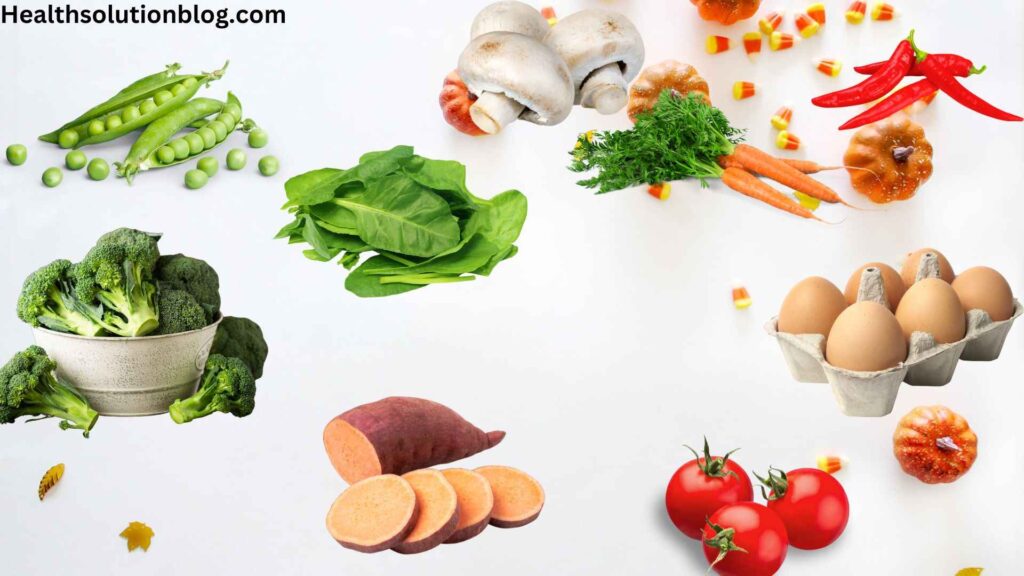

As we inquire into the world of melanin enhancement through food, let’s answer the main theme of our question, i.e., Which foods Increase Melanin in Skin?
Following are ten delectable and nutrient-rich foods that can support melanin production and promote radiant skin.
From vibrant fruits and vegetables to protein-rich sources and antioxidant powerhouses, each food brings a unique blend of nutrients that contribute to skin health and overall well-being.
5.1. Broccoli: A Cruciferous Vegetable Rich in Antioxidants
Broccoli, a cruciferous vegetable, is packed with antioxidants, including vitamin C and sulforaphane, which protect melanocytes from damage and promote melanin production. Its high fiber content also contributes to overall skin health.
5.2. Eggs: A Protein-Rich Food for Melanin Synthesis
Eggs are an excellent source of protein, a crucial building block for melanin synthesis. They also contain vitamin D, which plays a role in skin cell turnover and may indirectly support melanin production.
5.3. Red Peppers: A Source of Vitamin C for Melanin Production
Red peppers are a vibrant source of vitamin C, an antioxidant that may enhance melanin production and protect melanocytes from oxidative stress. Their high fiber content also promotes overall skin health.
5.4. Peas: A Versatile Legume Rich in Antioxidants
Peas, a versatile legume, is a good source of antioxidants, including vitamin C and vitamin E, which protect melanocytes from damage and may support melanin production. Their high fiber content also contributes to their overall skin health.
5.5. Plums: A Good Source of Vitamin C and Antioxidants
Plums, a sweet and juicy fruit, are a good source of vitamin C and antioxidants, which may enhance melanin production and protect melanocytes from oxidative stress. Their fiber content also promotes overall skin health.
5.6. Sweet Potatoes: Rich in Beta-Carotene for Melanin Synthesis
Sweet potatoes are an excellent source of beta-carotene, a precursor to vitamin A, which is essential for melanin production.
They also contain vitamin C and antioxidants, providing comprehensive skin support.
5.7. Carrots: A Crunchy Source of Beta-Carotene for Melanin Enhancement
Carrots, a crunchy and versatile vegetable, are rich in beta-carotene, a precursor to vitamin A, which plays a crucial role in melanin production.
They also contain vitamin C and antioxidants, promoting overall skin health.
5.8. Spinach: A Leafy Green Rich in Antioxidants for Melanin Support
Spinach, a leafy green powerhouse, is packed with antioxidants, including vitamin C and vitamin E, which protect melanocytes from damage and may support melanin production.
It’s also a good source of iron, which promotes healthy blood flow to melanocytes.
5.9. Mushrooms: A Vegetarian Source of Tyrosinase for Melanin Production
Mushrooms, a versatile culinary ingredient, are a good source of tyrosine, an amino acid that is a precursor to melanin.
They also contain antioxidants that protect melanocytes from damage and support overall skin health.
5.10. Tomatoes: A Rich Source of Lycopene for Melanin Protection
Tomatoes, a vibrant and versatile fruit, are rich in lycopene, an antioxidant that may protect melanocytes from sun damage and potentially support melanin production.
They also contain vitamin C and other antioxidants for overall skin health.
By incorporating these 10 melanin-boosting foods into your diet, you can provide your body with the nutrients it needs to support melanin production and maintain healthy, radiant skin.
Remember to combine dietary choices with sun protection and healthy lifestyle practices for optimal skin health.
6. Exploring Supplements for Melanin Enhancement
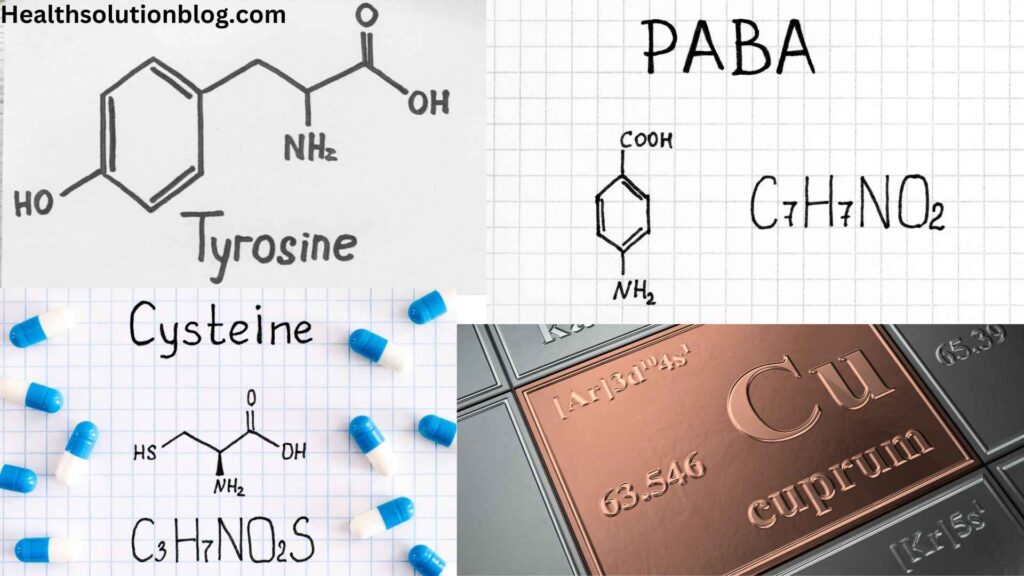
6.1. Understanding the Role of Supplements in Melanin Production
While dietary choices play a primary role in supporting melanin production, supplements may offer additional support in some cases.
Supplements can provide concentrated doses of specific nutrients that may contribute to melanin synthesis and skin health.
However, it’s crucial to approach supplements with caution and make informed decisions based on individual needs and potential risks.
Consulting with a healthcare professional can help determine if supplements are appropriate and guide you toward safe and effective options.
6.2. Considering Common Melanin-Enhancing Supplements
Several supplements are often touted for their potential to enhance melanin production. These include:
- Tyrosine: Tyrosine is an amino acid that serves as a precursor to melanin. Supplementing with tyrosine may theoretically increase melanin production, but evidence supporting its effectiveness is limited.
- L-cysteine: L-cysteine is another amino acid that may play a role in melanin synthesis. While some studies suggest potential benefits, more research is needed to confirm its efficacy.
- PABA (para-aminobenzoic acid): PABA is a precursor to folic acid, which may indirectly support melanin production. However, its effectiveness as a melanin enhancer remains unclear.
- Copper: Copper is a mineral involved in melanin synthesis. Supplementing with copper may be beneficial for individuals with copper deficiency, but over-supplementation can lead to adverse effects.
6.3. Weighing the Benefits and Risks of Supplements
While supplements may offer potential benefits for melanin enhancement, it’s crucial to weigh the risks and consider alternatives. Potential risks associated with supplements include:
- Side effects: Supplements can cause adverse effects, such as allergic reactions, digestive issues, and interactions with medications.
- Over supplementation: Excessive intake of certain supplements can lead to toxicity and potential health complications.
- Lack of regulation: Supplements are not as strictly regulated as prescription medications, and quality and purity may vary.
Before considering supplements, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional to assess individual needs, potential risks, and interactions with existing medications.
A balanced diet rich in melanin-boosting foods should be the primary approach to enhancing melanin production, with supplements considered as a complementary option only when appropriate.
7. Melanin and Skin Health: A Multifaceted Approach

7.1. Sun Protection: A Cornerstone of Skin Health
While melanin plays a crucial role in shielding our skin from the sun’s harmful UV rays, excessive sun exposure can still lead to damage.
Therefore, sun protection remains a foundation of skin health, regardless of melanin levels.
Seek shade during peak sun hours, wear protective clothing, and apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30 to all exposed skin.
Reapply sunscreen every two hours, or more often if sweating or swimming.
7.2. Moisturizing and Skin Care: Nurturing Your Skin
Maintaining a healthy skin barrier is essential for protecting against sun damage and promoting overall skin health.
A regular skincare routine that includes gentle cleansing, moisturizing, and using appropriate products for your skin type can help keep your skin hydrated, supple, and resilient.
Choose a moisturizer that suits your skin type and apply it generously to damp skin after cleansing.
Look for moisturizers that contain humectants, such as hyaluronic acid, to attract and retain moisture, and emollients, such as ceramides, to lock in moisture.
7.3. Seeking Professional Guidance: When to Consult a Dermatologist
While melanin provides a natural defense against sun damage, it’s not foolproof.
Consulting a dermatologist can help you assess your skin health, identify any potential concerns, and develop a personalized skincare plan.
If you notice any changes in your skin, such as new moles, asymmetrical moles, or changes in existing moles, seek professional advice promptly. Dermatologists can perform mole checks and other skin screenings to detect early signs of skin cancer.
Remember, melanin is a vital component of skin health, protecting us from the sun’s harmful rays. However, a multifaceted approach that combines melanin enhancement, sun protection, and proper skincare is essential for maintaining healthy, radiant skin throughout life.
8. Embracing Your Unique Skin Tone: A Celebration of Diversity

8.1. Understanding the Spectrum of Skin Tones
Human skin exhibits a remarkable diversity of tones, ranging from the fairest porcelain to the deepest ebony, each shade reflecting a rich tapestry of human heritage and genetic variation.
This spectrum of skin tones is a testament to the adaptability and resilience of our species.
Understanding the spectrum of skin tones is not merely about recognizing the physical differences but also appreciating the cultural and historical significance of skin color.
Skin tone has been used to categorize people, assign stereotypes, and even fuel discrimination.
However, in recent years, there has been a growing movement to challenge these outdated notions and celebrate the beauty and diversity of all skin tones.
8.2. Appreciating the Beauty of Diverse Skin
Each skin tone possesses its own unique beauty, radiating warmth, vibrancy, and individuality.
The rich types of melanin, the pigment that determines skin color, create a masterpiece of shades that reflect the diversity of human experience.
From the sun-kissed glow of olive skin to the luminous radiance of dark chocolate tones, each skin tone carries a story of its heritage, its ancestors’ journey across continents, and through time.
Appreciating the beauty of diverse skin is not just about aesthetics; it’s about recognizing the value and richness that each individual brings to the world.
8.3. Promoting Self-Acceptance and Inclusive Beauty Standards
For too long, narrow beauty standards have dictated the perception of beauty, often favoring lighter skin tones over darker ones.
This has led to feelings of insecurity and self-doubt among individuals with darker skin, continuing harmful labels and undermining their self-esteem.
Promoting self-acceptance and inclusive beauty standards is crucial to dismantling these harmful narratives and empowering individuals of all skin tones to embrace their unique beauty.
We must recognize that beauty is not defined by a single shade or feature but rather by the radiance of individuality, the confidence that comes from self-acceptance, and the appreciation for the diversity that makes us human.
In a world that often glorifies uniformity, embracing our unique skin tones is an act of rebellion, a celebration of our heritage, and a testament to the beauty that lies in diversity.
Let us move towards a future where the skin tone is not a source of division but a badge of honor, where every shade is celebrated and every individual feels empowered to shine in their own unique way.
Conclusion: Embracing Melanin and Celebrating Diversity
Melanin, the pigment that gives our skin its color, is not just a cosmetic feature; it’s a vital component of skin health, shielding us from the sun’s harmful UV rays.
Understanding the science behind melanin production and exploring natural ways to enhance melanin levels without compromising skin health is crucial for making informed decisions about our skin.
By incorporating melanin-boosting foods into our diets, adopting sun-protective practices, and maintaining a healthy skincare routine, we can empower our bodies to naturally enhance melanin production and promote radiant skin.
However, it’s essential to remember that true beauty lies in embracing our unique skin tones, celebrating the diversity that makes us human, and promoting self-acceptance and inclusive beauty standards.
How will you allow melanin to shape your story? Will you explore its potential for health and beauty, or will you revel in the uniqueness of your skin tone? Share your thoughts in the comments.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is melanin, and why is it important?
Melanin is a pigment that gives our skin its color. It also plays a vital role in protecting our skin from the sun’s harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays.
Q: What foods can help increase melanin production?
There are many foods that are rich in nutrients that can support melanin production. These include:
- Fruits and vegetables: Broccoli, spinach, carrots, sweet potatoes, red peppers, and plums
- Protein sources: Eggs, mushrooms
- Other: Tomatoes, peas
Q: Are there any supplements that can help increase melanin production?
There are some supplements that are sometimes touted for their potential to enhance melanin production, such as tyrosine, L-cysteine, and PABA (para-aminobenzoic acid). However, the evidence supporting their effectiveness is limited.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional before taking any supplements, as they can have side effects and interact with medications.
Q: What are some other things I can do to protect my skin from the sun?
In addition to eating a healthy diet, there are other things you can do to protect your skin from the sun, such as:
- Seeking shade during peak sun hours (10 am to 4 pm)
- Wearing protective clothing, such as a wide-brimmed hat and long sleeves
- Applying a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30 to all exposed skin every two hours, or more often if sweating or swimming
Q: When should I see a dermatologist?
You should see a dermatologist if you have any concerns about your skin, such as:
- New moles or changes in existing moles
- Skin cancer
- Other skin conditions, such as eczema or psoriasis
A dermatologist can help you assess your skin health and develop a personalized skincare plan.
Remember, melanin is a vital component of skin health, but it is important to take steps to protect your skin from the sun.
Sources:
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/how-to-increase-melanin





