Skin and hair are both important, especially for the beauty of the body. So it needs more care to be protected. Here I am giving detailed information about both these and “vitamins for glowing skin and glossy hair”.
So, from where are we going to start—skin or hair?

Well, I would prefer hair, though the skin is the largest organ of the body, but the body starts with hair, and everyone is more concerned about hair as baldness is the worst condition for anyone. I will also explain skin here, so don’t worry.
Can you tell us whether the hair is living or not?
Okay, If you are thinking it is living you are right, and if you are thinking it is dead, then you are also correct.
What?
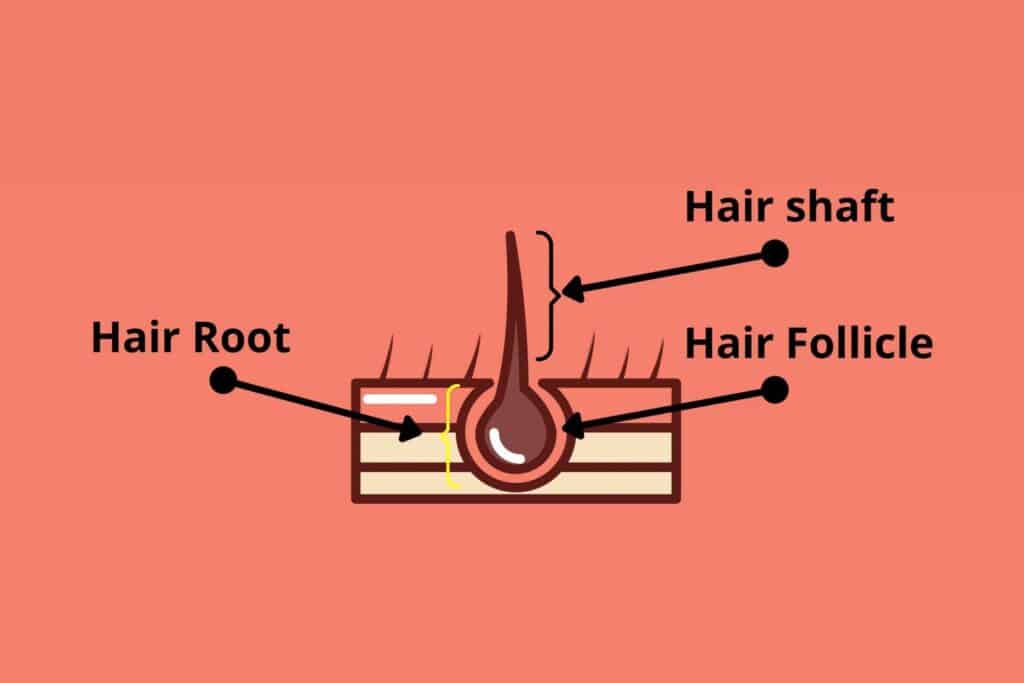
Calm down, I am explaining it to you. Hair has two parts, the visible part is called the hair shaft while the part of hair under the skin is called the hair root which has a tube-like opening called the hair follicle. There are about 1000000 hair follicles in every human.
Now how it is living and how it is dead?
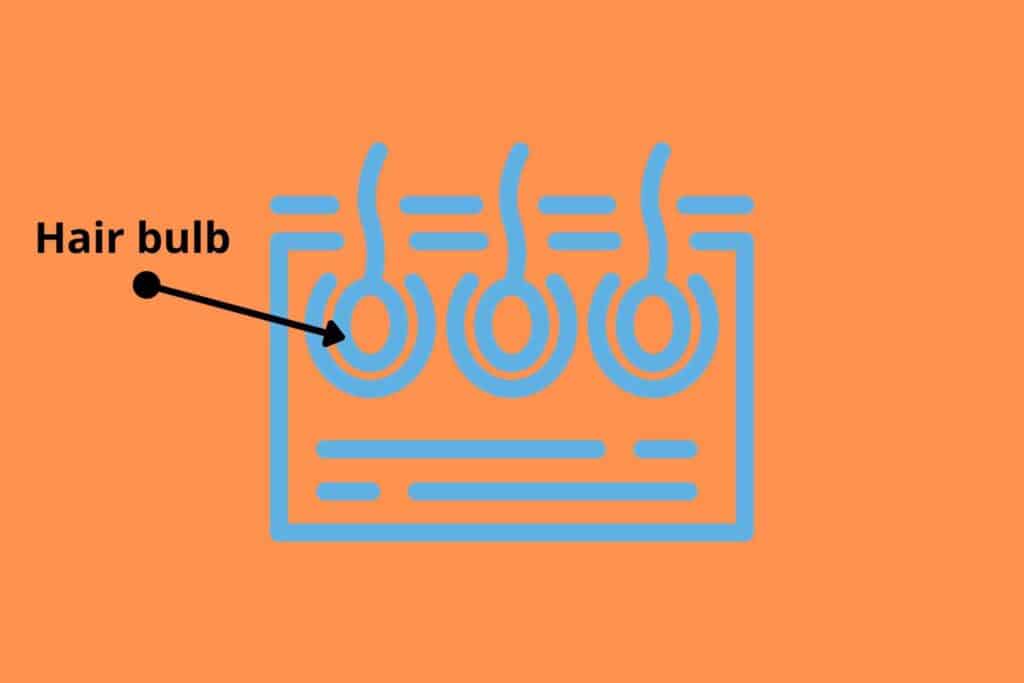
The hair follicle has a ball-like structure called the hair bulb where new cells form, because of the blood supply, showing living character, and as new cells form the old cells are pushed up through the root and become dead because of the cut of the blood supply.
Interesting…!
Oh, That’s why haircuts don’t pain?

Exactly, because the blood supply is cut after it is pushed to form the shaft, and that’s why it does not hurt while cutting, but pulling it makes the pain in the root, and of course, you feel it.
Can you tell me about the natural colors of hair?
Natural hair colors are the result of two types of melanin pigments.

This pigment is dominant in brown and black hair.
2. pheomelanin:

It is found in red hair.
But what about blonde and grey hair colors?
That’s a good question.
Blonde hair color:

This color is the result of having less pigmentation.
Grey hair color:

Grey hair color is due to the cessation of melanin production.
I would like to explain one more situation related to hair, that is,
Poliosis:
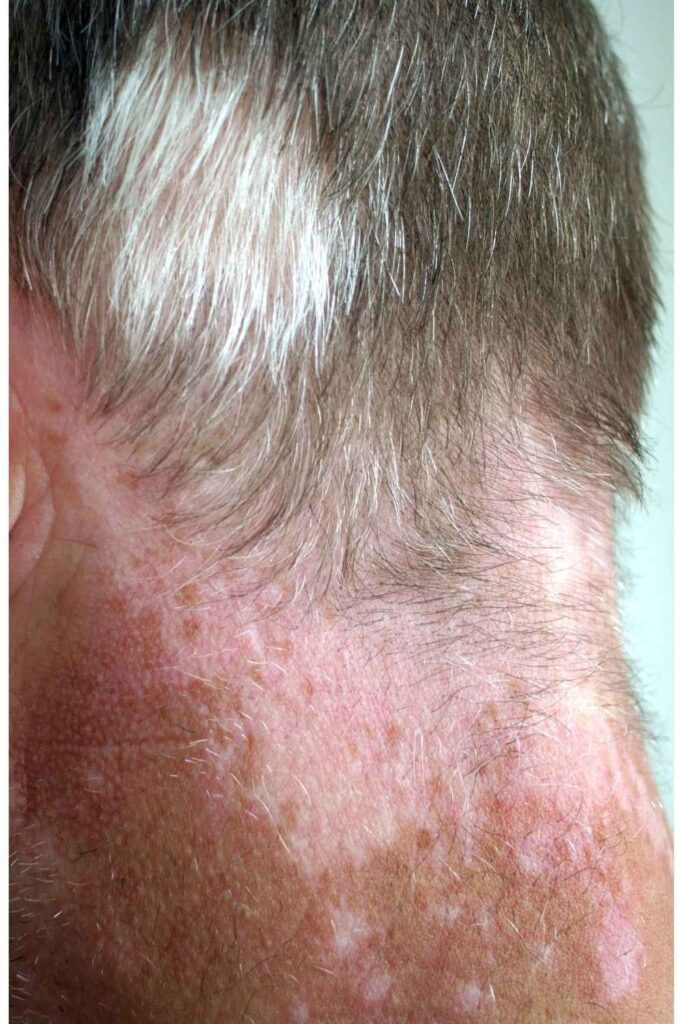
This condition occurs in hair or areas where hairs are attached, typically in spots where there is no melanin at all generally it is due to genetic reasons.
Now tell us about hair problems.
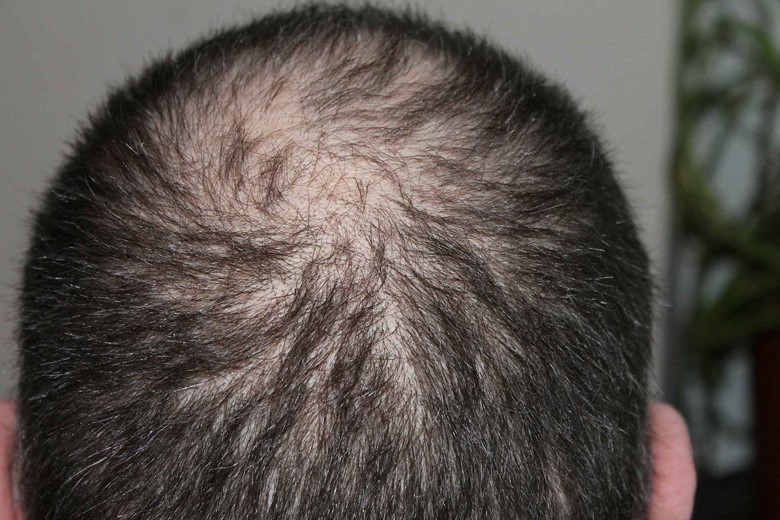
Hair loss and hair damage are the main problems, but if this condition is not present in someone, they should care for their hair before the worst situation comes.
How do hairs get damaged and lost?
Well, there are some reasons, which I am listing below.
- Ponytail exposure to severe heat, chemicals, dyes, or perms contributes to hair loss and damage.
- Medical conditions like thyroid problems (influence the whole metabolism of the body), chemotherapy, pregnancy, surgery, steroids, and depression lead to hair damage.
- Deficiency in essential nutrients also causes hair damage.
Now how can we make our hair healthier?
Okay, let’s start with minerals.
Minerals:
Iron:
Iron is the core element of hemoglobin, and hemoglobin carries oxygen and nutrients to the cells, so if there is a deficiency of iron, the whole body will be affected, and also hairs will be affected so for proper growth iron is necessary.
Source:
- Fortified breakfast cereals
- Cooked oysters
- White beans
- Dark green leafy vegetables
- Apples
- Banana
- Pomegranate
- Mulberry
Zinc:

Zinc plays a key role in tissue repair, hair repair, and protein syntheses such as keratin and collagen, which support hair, nails, and skin. Zinc deficiency leads to the weakening of proteins in hair follicles, which eventually results in hair loss.
Here I would say that women who have regularly heavy menstrual cycles can have a deficiency of zinc in their bodies, So women need special focus on their diet.
Source:
- Bean
- Tofu
- Sweet corn
- Red meat
- Poultry
- Liver
- Prawns
Silica:

Silica makes the hair thicker, retains its elasticity, and increases its volume. Research at the University Hospital of Hamburg-Eppendorf shows that the use of silica gel makes thinner hair thicker by 13 percent.
Source:
- Green beans
- Leeks
- Grain bread
- Pasta
- Oatmeal
- Brown rice
- Banana
- Mangoes
- Spinach
- asparagus
Vitamins:
Biotin

Biotin is also known as vitamin B7.

It strengthens the development of hair follicles, particularly those of damaged or lacking-strength hairs, and reduces hair fall.
Biotin with chromium picolinate (mineral) help type II diabetic patient lower their glucose level.
Source:
Almonds, peanuts, soybean, banana, oats, salmon, egg yolk, spinach, sweet potato, and cheese have biotin in sufficient amounts.
Vitamin A:
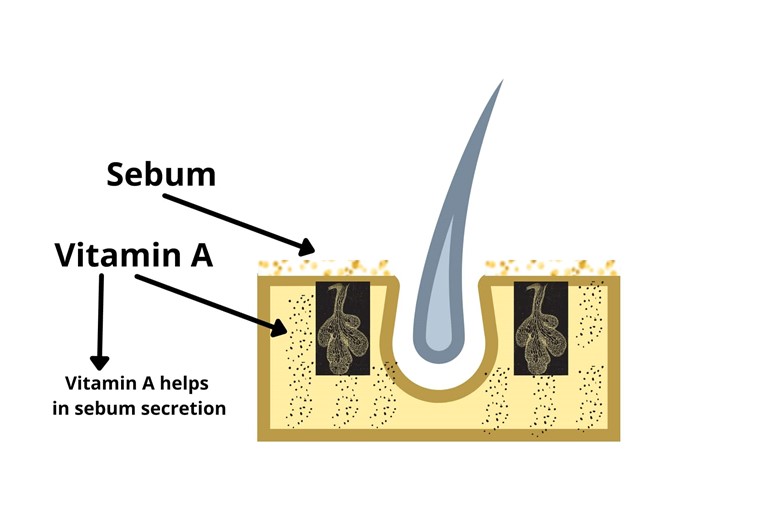
Vitamin A helps the skin gland secrete an oily substance called sebum to moisturize the skin, so vitamin A deficiency leads to dry hair and a dry scalp, which ultimately results in hair loss.
But here is one important thing to be noted: studies show that too much vitamin A also leads to hair loss. It must be taken care of to check the balance.
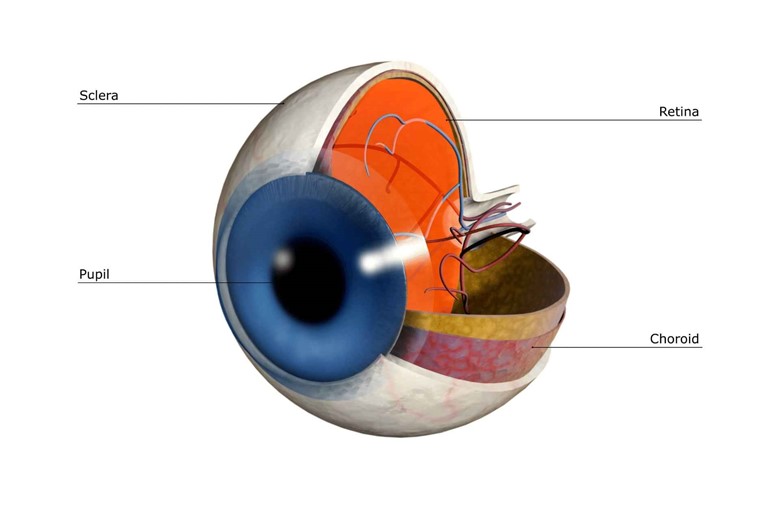
Vitamin A is also known as retinol; the name was given because of its major role in retinal support, i.e., vision.
Source:
- Eggs
- Cod liver oil
- Beef liver
- Sweet potatoes
- carrots
- Fortified skim milk
- Spinach
- Broccoli
- orange
Vitamin C:
Free radicals are atoms or molecules formed in the cell due to normal metabolism and are present in food, air, drugs, etc. These free radicals have unpaired electrons and are highly reactive, damaging the cell by stealing electrons from mitochondria and membranes through the process of oxidation.
Vitamin C is an antioxidant, thus protecting the cells from damage and making hair healthier.
Source:
- Citrus fruits, such as
- Oranges
- Kiwi
- Guava
- strawberries
- Grapefruits
- Broccoli
- Cauliflower
Vitamin D:

Vitamin D may help to create new follicles from where hair grows (hair regrows).
Source:
- Salmon
- Cod liver oil
- Egg yolk
- Canned tuna
- Mushrooms
- Fortified foods
Vitamin E:

Vitamin E is also an antioxidant, like vitamin C. It repairs damaged hair follicles, promotes blood circulation, and acts as a deep moisturizer for hair, preventing breakage and brittle hairs.
Vitamin E also protects your hair from the sun’s effects.
Sources:
- Vegetable oil (such as sunflower, safflower, corn, and soybean oil)
- Almond
- Peanuts
- Hazelnut
- Spinach
- Broccoli (green leafy vegetables)
- Fruit juices
Can you tell the difference between minerals and vitamins?
Well, the main difference between minerals and vitamins is:
Minerals are inorganic and can be held in their chemical structure by heat, e.g. calcium, zinc, potassium, silicon, etc.
While vitamins are organic and can be broken down by heat,. e.g., vitamins A, B, C, D, and E.
That’s interesting.
Now come to the skin?
Oh, yes, why not?
The largest organ of the body that covers the whole body is the skin.
Which nutrients are best for glowing skin?
The first inorganic I recommend, not only for the skin but for the whole body, is water, which is considered life.
Water?

Yes, the water!.
Water:
Water is crucial for our body, and some of its effects on our skin are described here.
i) Fewer wrinkles:
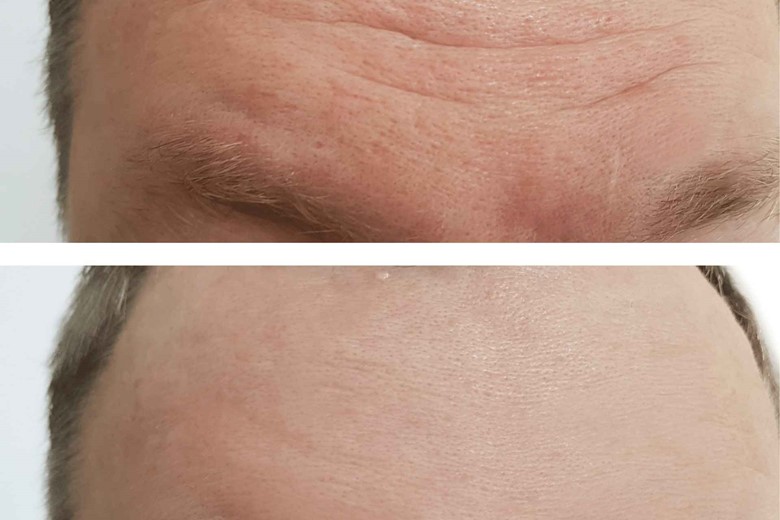
Water helps to moisturize your skin, which means more elasticity and fewer wrinkles and lines on your skin.
ii) Remove toxins:
Drinking sufficient water combats a variety of diseases like eczema (Inflamed, red, itchy, cracked, and rough skin) and psoriasis (red, itchy, scaly patches on the skin) by removing toxins from the body through the digestive system.
Thus making skin complexion improve and glowing appearance.
iii) Increase blood flow to the skin:
Drinking 2 cups of water (daily 8 glasses of water are recommended) increases blood flow to the skin leading to glowing and complexion effects.
iv) Clear Acne:
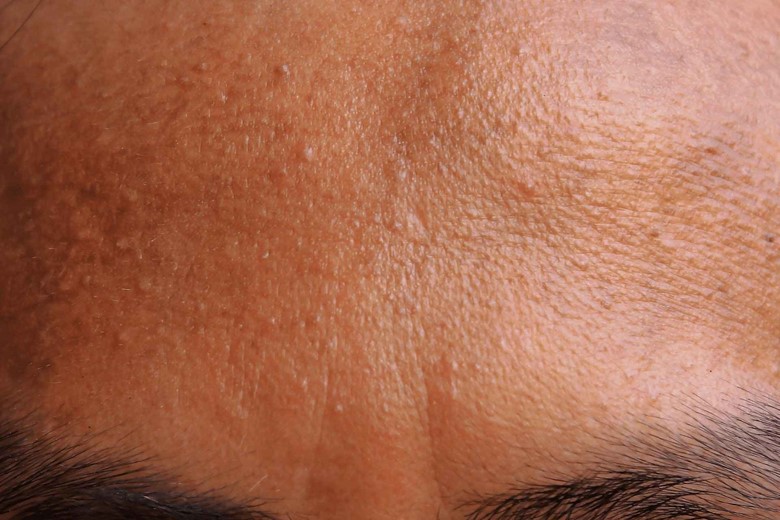
Water flushes out the toxins from the body and shrinks the pores making skin free of acne.
v) Slow aging:

Water makes the cell swell and gives a chubby appearance which doesn’t allow the wrinkles to appear and also minimizes the existing wrinkles if any.
vi) Drain itchiness:

Some skins are dry and they can easily flake, crack, and itch. So if you have this condition then take more water because water will make your skin hydrated and there is very little chance of cracking and itching.
Iron (Fe):

Iron (Fe) gives a glowy appearance to the skin and makes the wound heal fast because it transports oxygen to all cells so if sufficient oxygen reaches the cell it means more energy to the cell.
Iron deficiency causes anemia with pale skin.
Zinc:
Zinc helps the skin in several ways.

- Zinc Kills those bacteria that cause acne (Propionibacterium acnes or Cutibacterium acnes).
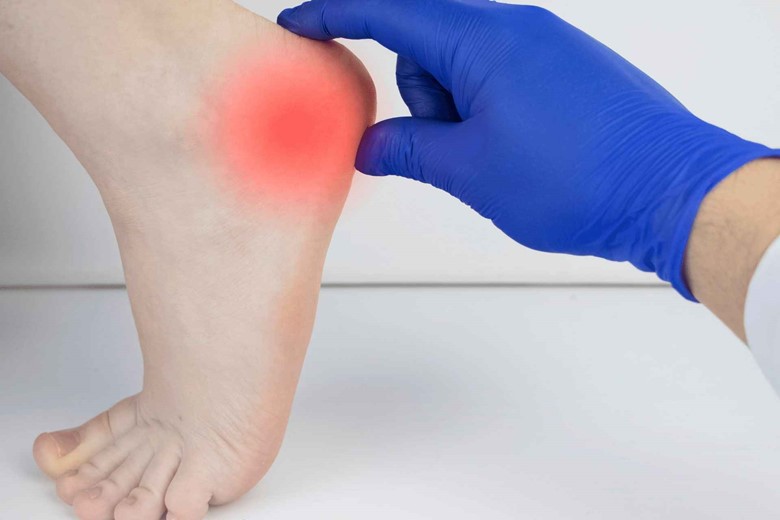
- Anti-inflammatory effect for inflammatory acne or scarring.
- Control the production of keratin (a protein that binds the cells together). Their excess causes blockage of pores and acne.
- Regulate the activity of oil glands.
Let’s come to vitamins.
Vitamin A:
Vitamin A helps to prevent the skin from drying out through the process of tissue repair, produces new skin cells, supports collagen production, and controls keratin.
I would like to tell you one important thing about vitamin A deficiency and excess.
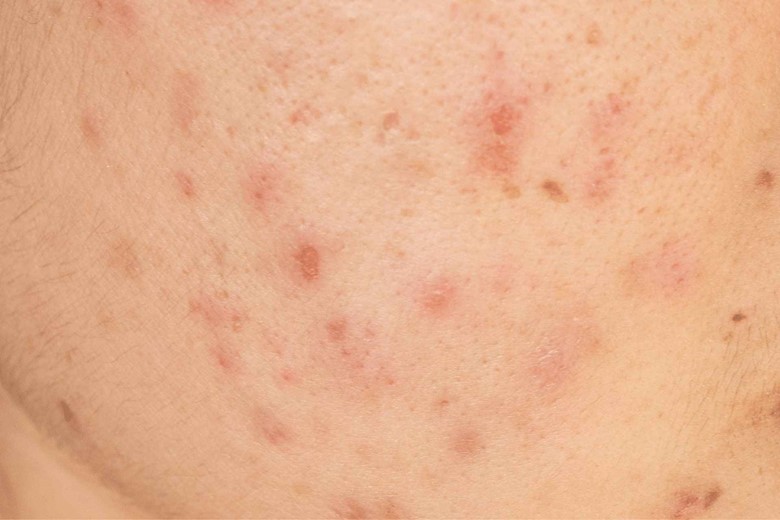
while uptake of too much retinyl palmitate (a form of vitamin A) according to the U.S. government, says, may increase the chance of skin lesions and skin tumors when applied in the presence of sunlight.
Follicular hyperkeratosis is a condition that is caused by vitamin A deficiency, in which there is too much keratin in follicles which causes papules on the skin.
Sources:
- Dairy products
- Eggs
- Salmon
- Beef liver
- Cod liver oil
- Shrimp
- Carrots
- Tomatoes
- Sweet Potatoes
- Leafy green vegetables
- Mangoes
- Apricot
- Plums
- Watermelon
Vitamin B complex:

Vitamin B complex is not just one vitamin, it is a combination of many classes of vitamin B.
Names with functions are mentioned below.
Vitamin B1:

Also known as thiamin. It is involved in the functioning of the nervous system and has antioxidant and antiaging effects too.
Deficiency:
Deficiency can cause hypersensitivity to the skin making it more sensitive to products and climate which leads to redness, acne, and flaky skin.
Source:
- Beef
- Liver
- Nuts
- Oat
- Seeds
- Legumes
- Peas
- Cauliflower
- Oranges
Vitamin B2:

Another name is riboflavin, which plays a stunning role in keeping glowing skin. It maintains tissue growth giving a glowy appearance to the skin.
This is the best vitamin for acne-prone skin because it supports the skin to secrete mucus to prevent acne and dry skin.
Deficiency:
Symptoms are Cracked skin and lips specifically in the corner of the mouth.
Source:
- Almond
- Mushroom
- Spinach
Vitamin B3:

The other name is niacinamide which retains skin moisture thus removing wrinkles and slowing the aging process.
Vitamin B3 also minimizes the inflammatory diseases of skin like redness, eczema, acne, and rosacea, So it is best for dry, sensitive, and aging skin.
Vitamin B5:

Commercially known as pantothenic acid. It has soothing, moisturizing, healing, and regenerating properties. It also improves the elasticity of the skin by retaining moisturization, thus reducing signs of aging.
Source:
- Mushroom
- Avocados
- Tomatoes
- Shellfish
- Chicken
- Milk
- Yogurt
Vitamin B6:
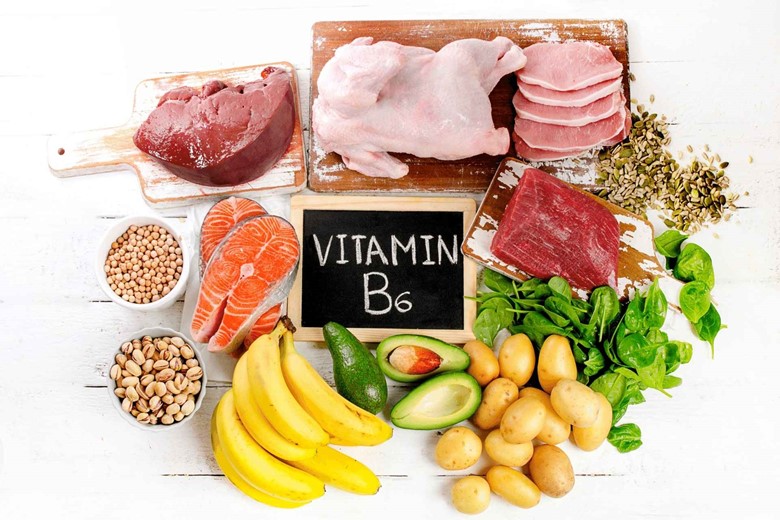

Also known as pyridoxine, acts as a coenzyme in the production of haem of hemoglobin. Control prostaglandin activity and reduce testosterone thus preventing this hormonal imbalance which would cause acne if not controlled.
It also controls happy, sad, and stressful moods (hormones) which if not controlled can lead to premature aging.
Source:
- Banana
- Garbanzo beans
- Chicken or turkey
- Soya bean
- Eggs
- Whole grain cereals
Vitamin B7:

Commonly known as Biotin. Once it was known as vitamin H. The H stands for Haar and Haut, which is German for hair and skin. It helps in cell repair, amino acid, and fatty acid synthesis. It also helps, to remove dermatitis, rashes, eczema, and acne from the skin.
Source:
- Oatmeal
- Almonds
- Walnuts
- Peanuts
- Cereals
- Egg yolk
- cauliflower
- mushrooms
Vitamin B9:
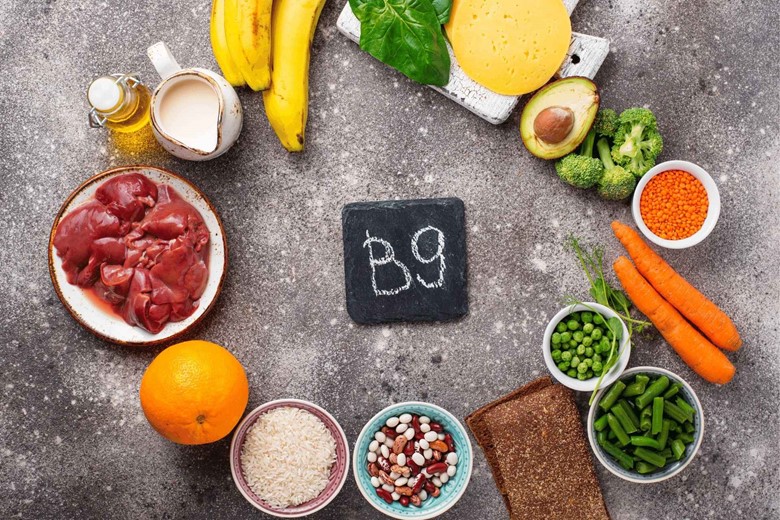

Vitamin B9 also called folic acid which keeps healthy cells turned over by cell and tissue production. It also contributes to glowing, healthy skin that looks radiant, clear, and plumpy.
Note: Be careful overloading folic acid can lead to dry, patch, and increased acne on the skin. It should not be increased by 500 micrograms.
Source:
- Garbanzo beans
- Spinach
- Lentils
- Asparagus
- Yeast
- Oranges
- Strawberries
Vitamin B12:

Another name for vitamin B12 is cobalamin. Vitamin B12 is necessary for cell reproduction and reduces dryness, inflammation, and acne.
Source:
- Fish
- Poultry
- Milk products
- Meat
- Cheese
Vitamin C:

Vitamin C is an antioxidant that neutralizes free radicals to regenerate damaged skin cells, support collagen production, and heal wounds in the skin.
Source:
- Orange
- Kiwi
- Lemon
- Guava
- Grapefruits
- Broccoli
- Cauliflower
- Capsicum
Vitamin D:

Too much exposure to the sun speeds up premature skin aging but vitamin D might help in preventing this aging. It also helps with skin protection and rejuvenation.
Source:
- Fatty fish like tuna, mackerel, and salmon.
- dairy products
- orange juice,
- soy milk
- Cereals.
- Beef liver.
- Cheese.
- Egg yolks.
Vitamin E:

It is also an antioxidant and gives healing support for burns and scars.
- NOTE: Vitamin E is not advisable for supersensitive skin, very oily, or acne-prone skin because it may cause rashes, irritation, or itching to the skin but it is very uncommon, found in about 1% of people.
These are very interesting details.
Could you please tell us what nutrients are most important, best, and common for both skin and hair?
Well, Both are very close and require almost equal nutrients. But here I am giving the most important nutrients for both i.e 2 in one.
Iron:
To the skin, iron gives a glowy appearance and makes hair strong. As it is the core element of iron that transports oxygen to every cell.
Zinc:

In the case of hairs, it is a repairer of hairs by the synthesis of keratin and collagen (the main constituent of hairs, nails, etc), nourishing hair follicles while in the case of skin, it has an anti-inflammatory effect on inflammatory acne or scarrings, regulate oil glands and kills the bacteria which cause acne (Propionibacterium acnes or Cutibacterium acnes).
Menstruation women have a specific deficiency of zinc so they need more care.
Vitamin A:
As it secretes mucus and makes skin moisturized it is necessary for both hairs and skin because of dry scalp damage to hair and also to the skin. Also, it is necessary for vision, the immune system’s proper work, and skin repair.
Now let’s jump to the second important nutrient.
We are eagerly waiting for this.
That is Vitamin B.
Biotin or vitamin B7:
Once it was known as vitamin H. The H stands for Haar and Haut, which is German for hair and skin. It is a nutrient for skin and hair.
It strengthens the development of hair follicles, particularly hair follicles of damaged or lacking-strength hairs and reduces hair fall.
And for skin, It helps, to remove dermatitis, rashes, eczema, and acne from the skin.
Vitamin C:
Vitamin C is an antioxidant and fights against free radicals in the cell thus making much of their important for healthier hair, and glowy skin by regeneration of skin cells, healing wounds, and supporting collagen production.
Vitamin E:
It is also an antioxidant. Besides these, it also regenerates hair follicles, promotes blood circulation, and prevents breakage of brittle hair by acting deep moisturizer for hair.
For skin, it supports the healing of scars and burns.
What is the daily amount of these nutrients?
This is a very necessary question.
Iron daily intake level:
| Age | Male | Female | Pregnancy | Lactation |
| Birth to 6 months | 0.27 mg* | 0.27 mg* | ||
| 7–12 months | 11 mg | 11 mg | ||
| 1–3 years | 7 mg | 7 mg | ||
| 4–8 years | 10 mg | 10 mg | ||
| 9–13 years | 8 mg | 8 mg | ||
| 14–18 years | 11 mg | 11 mg | 27 mg | 10 mg |
| 19–50 years | 8 mg | 18 mg | 27 mg | 9 mg |
| 51+ years | 8 mg | 8 mg |
ZINC daily intake requirement:
| Life Stage | Recommended Amount |
| Birth to 6 months | 2 mg |
| Infants 7–12 months | 3 mg |
| Children 1–3 years | 3 mg |
| Children 4–8 years | 5 mg |
| Children 9–13 years | 8 mg |
| Teens 14–18 years (boys) | 11 mg |
| Teens 14–18 years (girls) | 9 mg |
| Adults (men) | 11 mg |
| Adults (women) | 8 mg |
| Pregnant teens | 12 mg |
| Pregnant women | 11 mg |
| Breastfeeding teens | 13 mg |
| Breastfeeding women | 12 mg |
Vitamin A daily intake requirement:
| Life Stage | Recommended Amount |
| Birth to 6 months | 400 mcg RAE |
| Infants 7–12 months | 500 mcg RAE |
| Children 1–3 years | 300 mcg RAE |
| Children 4–8 years | 400 mcg RAE |
| Children 9–13 years | 600 mcg RAE |
| Teens 14–18 years (boys) | 900 mcg RAE |
| Teens 14–18 years (girls) | 700 mcg RAE |
| Adults (men) | 900 mcg RAE |
| Adults (women) | 700 mcg RAE |
| Pregnant teens | 750 mcg RAE |
| Pregnant women | 770 mcg RAE |
| Breastfeeding teens | 1200 mcg RAE |
| Breastfeeding women | 1300 mcg RAE |
Note: micrograms (mcg) of retinol activity equivalents (RAE).
Vitamin B7 or Biotin daily intake requirement:
| Age | Male | Female | Pregnancy | Lactation |
| Birth to 6 months | 5 mcg | 5 mcg | ||
| 7–12 months | 6 mcg | 6 mcg | ||
| 1–3 years | 8 mcg | 8 mcg | ||
| 4–8 years | 12 mcg | 12 mcg | ||
| 9–13 years | 20 mcg | 20 mcg | ||
| 14–18 years | 25 mcg | 25 mcg | 30 mcg | 35 mcg |
| 19+ years | 30 mcg | 30 mcg | 30 mcg | 35 mcg |
Vitamin C daily intake requirement:
| Age | Male | Female | Pregnancy | Lactation |
| 0–6 months | 40 mg* | 40 mg* | ||
| 7–12 months | 50 mg* | 50 mg* | ||
| 1–3 years | 15 mg | 15 mg | ||
| 4–8 years | 25 mg | 25 mg | ||
| 9–13 years | 45 mg | 45 mg | ||
| 14–18 years | 75 mg | 65 mg | 80 mg | 115 mg |
| 19+ years | 90 mg | 75 mg | 85 mg | 120 mg |
Vitamin E daily intake requirement:
| Age | Males | Females | Pregnancy | Lactation |
| 0–6 months* | 4 mg | 4 mg | ||
| 7–12 months* | 5 mg | 5 mg | ||
| 1–3 years | 6 mg | 6 mg | ||
| 4–8 years | 7 mg | 7 mg | ||
| 9–13 years | 11 mg | 11 mg | ||
| 14+ years | 15 mg | 15 mg | 15 mg | 19 mg |
Conclusion:
I am sure every one of you knows that excess or decline of anything from the normal level is harmful so use it carefully. So keep your regular balanced diet but if you find any symptoms explained above then consult a doctor and take it. But to make hair glossy and skin glowy then you should take the important nutrients I have explained in the “Could you please tell us what nutrients are most important, best, and common for both skin and hair?” section. You have to take nutrients or supplements at a high level when there is a deficiency in your body. Unnecessary taking causes problems in the body like excess calcium making kidney stones. Here I am giving the best supplement for glossy hair and glowing skin.
Here are the multivitamins minerals for your family’s hair and skin.



