“Tanning” refers to the process of skin darkening due to exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or artificial sources. It occurs when the skin produces more melanin, resulting in a darker color.
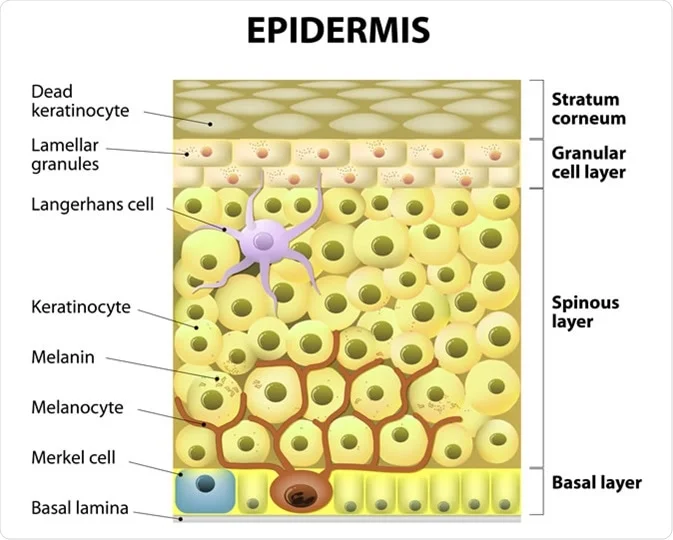
Melanin is the pigment that gives skin its color, and it’s produced by cells in the epidermis called melanocytes. The amount of melanin that is produced depends on several factors, including your skin type, age, and sun exposure.
Some people believe that tanning stops when your skin reaches a certain point, but this is not always the case. In fact, there are many things you can do to enhance your tan and make it last longer.
In this article, we will discuss the factors that can affect your ability to tan, including your age, skin type, and sun exposure. We will also provide tips on how to get a natural tan safely.
So, Does your skin stop tanning at a certain point?
The answer is yes, but it depends on several factors. Following are the factors with suggestions to avoid or get that.
1. Hydration:
Skin hydration levels can also affect the ability to tan. When your skin is dehydrated, it produces less melanin, which can make it more difficult to tan.
Additionally, dehydrated skin is more likely to become sunburned and flaky, which can further damage your skin and make it more difficult to tan in the future.
Here are some tips for keeping your skin hydrated:
A. Drink plenty of water.

Aim for at least eight glasses of water per day.
B. Use a moisturizer.

Choose a moisturizer that’s right for your skin type.
C. Avoid excessive sun exposure.

Wear sunscreen whenever you’re outside, especially at midday.
D. Take breaks from the sun.

If you’re going to be in the sun for an extended period, take breaks every hour or two to get out of the sun and cool down. Also, apply sunscreen while in the sun.
By following these tips, you can keep your skin hydrated and healthy, which will help you tan more easily and safely.
2. Age:

With age, the skin produces less melanin, so you may not tan as easily.
Also, the underlying layer of skin, called the dermis, becomes less vascular as we age. This means that there is less blood flow to the skin, which can make it more difficult for the skin to tan.
Here are some tanning tips to safely use as you age:
- Wear sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher.
- Avoid tanning during the middle of the day, when the sun’s rays are strongest.
- Take breaks from the sun every hour or two.
- Listen to your body and stop tanning if you feel uncomfortable.
If you’re concerned about your ability to tan safely, talk to your doctor. They can help you determine if any underlying medical conditions are affecting your tanning ability.
3. Skin type:
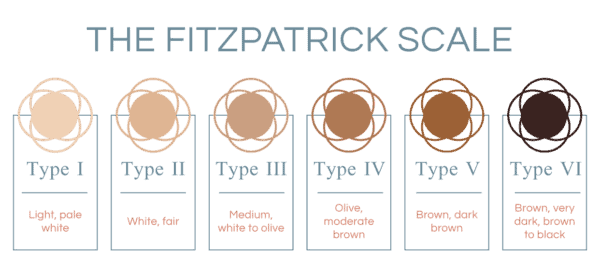
People with darker skin types tend to tan more easily than people with lighter skin types. This is because people with darker skin have more melanin, which is the pigment that gives skin its color and helps protect it from the sun’s harmful UV rays.
Dark-skinned people are found in warmer countries where sun rays are strong, so this is an adaptation against sun-damaging rays.
Here is a table that summarizes the different skin types and how they affect tanning:
| Skin Type | Description | How it Affects Tanning |
|---|---|---|
| Fitzpatrick Skin Type I | Very fair skin that burns easily and rarely tans. | People with Fitzpatrick Skin Type I are the least likely to tan. |
| Fitzpatrick Skin Type II | Fair skin that burns easily and tans minimally. | People with Fitzpatrick Skin Type II are less likely to tan than people with Fitzpatrick Skin Type I, but they are still more likely to tan than people with darker skin types. |
| Fitzpatrick Skin Type III | Light to medium skin that burns moderately and tans gradually | People with Fitzpatrick Skin Type III are more likely to tan than people with Fitzpatrick Skin Type I or II, but they are still less likely to tan than people with darker skin types. |
| Fitzpatrick Skin Type IV | Medium to olive skin that rarely burns and tans easily. | People with Fitzpatrick Skin Type IV are the most likely to tan. |
| Fitzpatrick Skin Type V | Olive to brown skin that rarely burns and tans very easily. | People with Fitzpatrick Skin Type V are the most likely to tan. |
| Fitzpatrick Skin Type VI | Black skin that never burns and tans very easily. | People with Fitzpatrick Skin Type VI are the most likely to tan. |
As mentioned earlier, people with darker skin types are more likely to tan than people with lighter skin types. However, it is still important to wear sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher, even if you have naturally dark skin.
4. Sun exposure:

The more time you spend in the sun, the more likely you are to tan. However, excessive sun exposure can damage your skin and increase your risk of skin cancer by damaging the DNA.
5. Genetics:

Genetics also play a role in how easily you tan. Your genes determine how much melanin your skin produces, which affects how dark your skin will become when you’re exposed to the sun.
People with genes that code for more melanin are more likely to tan easily than people with genes that code for less melanin.
6. Medications:
Medications can also affect your tanning ability. Some medications can make your skin more sensitive to the sun, which can make it more difficult to tan. Other medications can make your skin tan more easily.
Here are some examples of medications that can affect your ability to tan:
I. Antibiotics:
Some antibiotics, such as tetracycline, can make your skin more sensitive to the sun.
II. Antihistamines:
Some antihistamines, such as diphenhydramine (Benadryl), can also make your skin more sensitive to the sun.
III. Blood pressure medications:
Some blood pressure medications, such as hydrochlorothiazide (HydroDIURIL), can make your skin more sensitive to the sun.
IV. Photosensitizing medications:
Some medications, such as psoralen and ultraviolet A (PUVA) therapy, are used to treat skin conditions such as psoriasis. These medications can make your skin more sensitive to the sun, which can make it more difficult to tan.
Here are some additional tips about medications and tanning:
- Sunscreen is still important to use, even if you’re taking medications that make your skin more sensitive to the sun.
- Wear protective clothing, such as a hat and sunglasses, when you’re in the sun.
- Avoid tanning during the middle of the day, when the sun’s rays are strongest.
- Take breaks from the sun every hour or two.
- Listen to your body and stop tanning if you feel uncomfortable.
It’s important to protect your skin from the sun’s harmful UV rays, even if you’re taking medications that make your skin more sensitive to the sun. Sunscreen is the best way to protect your skin from the sun. You should also wear protective clothing, such as a hat and sunglasses when you’re in the sun.
7. Medical conditions:
Some medical conditions, such as vitiligo, can make it difficult to tan.
What are the signs that your skin is no longer tanning?
There are a few signs that your skin is no longer tanning, i.e.:
- Your skin stops getting darker after spending time in the sun.
- Your tan starts to fade more quickly.
- You start to develop freckles or age spots.
But why am I not tanning anymore?
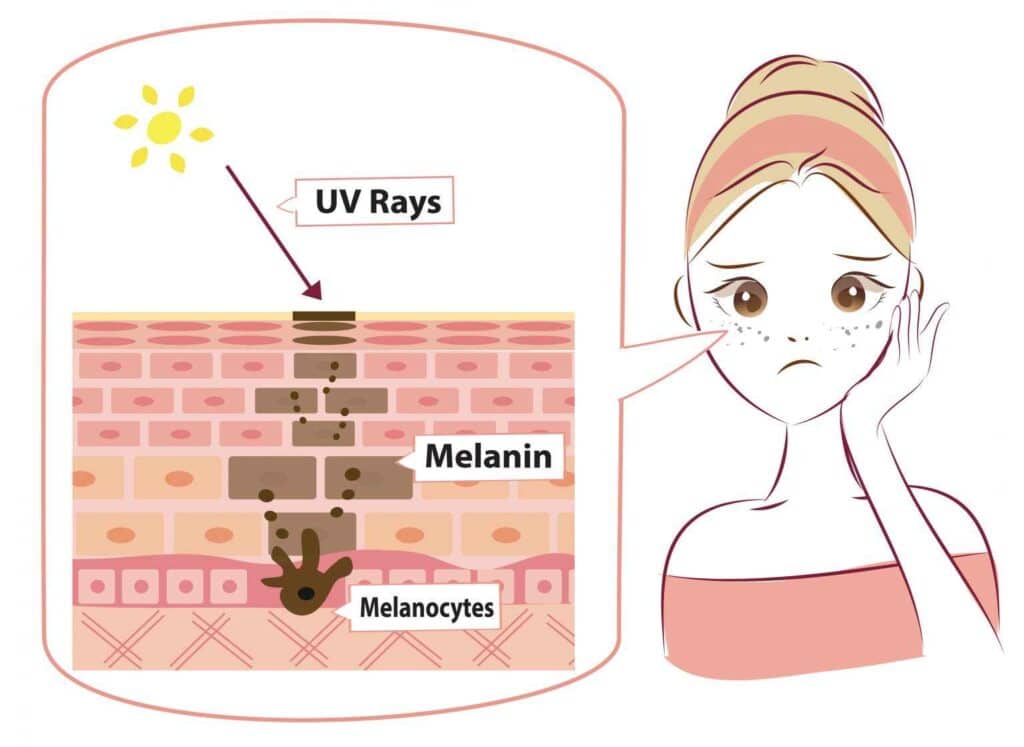
Tanning plateau is the most common reason why people stop tanning or no longer get any darker. It is the point at which skin stops producing more melanin, the pigment that gives your skin its color. Everyone has their tanning plateau, and the amount of time it takes to reach it can vary.
Other reasons why you may not be tanning properly include age, health conditions, the products you are using, and medications. If you are concerned about why you are not tanning anymore, it is a good idea to talk to your doctor. They can help you determine the cause and recommend safe ways to get a tan if you still want to.
Other factors like age, hydration, sun exposure, genetics, medications, and medical conditions are the main reasons for not tanning anymore which is already explained above.
Is there any problem with not tanning anymore?

There are no major health problems associated with not tanning anymore. In fact, there are many potential benefits to avoiding tanning, including:
i. Reduced risk of skin cancer:
Tanning beds and the sun emit harmful UV rays that can damage your skin and DNA and increase your risk of skin cancer. Avoiding tanning can help reduce your risk of developing this serious disease.
ii. Less premature aging:
UV rays can also damage the collagen and elastin in your skin, which can lead to premature aging. Avoiding tanning can help keep your skin looking younger and healthier for longer.
iii. Better overall health:
Tanning can also suppress your immune system and make you more susceptible to infections. Avoiding tanning can help keep you healthier overall.
But if people want to maintain their tanned glowy look, how can they do that?

There are a few ways to maintain a tanned glow without exposing your skin to harmful UV rays. Here are a few options below:
a. Self-tanners:
Self-tanners are a safe and effective way to get a tan without the risks associated with natural tanning. There are a variety of self-tanners available. The following is one of the best among them.
- NATURAL, NOT ORANGE! --stay confident with a natural looking tan. This green-based solution counteracts the fake orange tan look that can often be an issue with other self tanners. Apply Californium at night and shower in the morning to achieve a natural, gorgeous glow without streaks or blotches.
- SAFE SUNLESS TAN - Californium is perfect for lighter skin tones, and is the best way to get a healthy, natural glow for up to 7 days without exposing your skin to harmful UV rays that can cause premature wrinkles and skin cancer. Californium contains as many natural and organic ingredients as possible for the safest tan possible.
- ONE PRODUCT FOR FACE AND BODY – Skinerals Californium is ideal for both the face and body. There is no need to purchase a second product for your face as this product is non-greasy, doesnt cause acne, and can be applied under makeup.
- ENJOY HAPPY, YOUTHFUL SKIN - Our bronzers contain antioxidants such as acai berry and fig extracts to help even out skin tone and reduce the appearance of blemishes and stretch marks. These ingredients combined with avoidance of sun damage will keep your skin looking youthful. This is a USA made cruelty-free, sulfate-free, paraben-free, aerosol-free, and vegan skincare solution.
- EASY APPLICATION WITHOUT TRANSFER – This lightweight and non-sticky formula dries in minutes and is best applied with the Skinerals Microfiber Applicator Mitt for a smooth, consistent application without the mes
Prices pulled from the Amazon Product Advertising API on:
Product prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.
b. Bronzers:
Bronzers can also help to create a tanned glow. Bronzers are typically powders or creams that are applied to the skin to give it a darker, more sun-kissed appearance.
c. Tanning drops:
Tanning drops are a newer product that is gaining popularity. Tanning drops are added to your moisturizer or foundation to give your skin a subtle, natural-looking tan.
- Easy to use, refreshing self-tanning waters are the most hydrating way to glow.
- Color-correcting self-tan drops for face and body that you mix with your favorite moisturizer or body care for a custom glow.
- Transform your favourite skincare into a custom self-tanner.
- Travel Friendly
- Add 2-12 drops to a minimum of 1/2 tsp. of your favorite moisturizer, mix together, and apply to skin. These drops are a concentrate and must always be mixed with a moisturizer! Wash hands after applicatio
Prices pulled from the Amazon Product Advertising API on:
Product prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.
d. Vitamin D:
Vitamin D is essential for good health, and it can also help to give your skin a healthy glow. You can get vitamin D from sunlight, but you can also get it from fortified foods and supplements.
- Immune Support: According to The Scientific American, Three-quarters of U;S; teens and adults are deficient in vitamin D, the so-called sunshine vitamin whose deficits are increasingly blamed for everything from cancer and heart disease to diabetes; vitamin d deficiency is a serious health concern that could be affecting your health; Many people use vitamin d cream for alopecia and to greatly strengthen their immune systems to fight off colds, sickness, and disease
- Maximum Absorption With Aloe Vera, MSM, Coconut Oil, Shea Butter
- IMMUNE SUPPORT: According to The Scientific American, Three-quarters of U;S; teens and adults are deficient in vitamin D, the so-called sunshine vitamin whose deficits are increasingly blamed for everything from cancer and heart disease to diabetes
- IMMUNE SUPPORT: According to The Scientific American, Three-quarters of U;S; teens and adults are deficient in vitamin D, the so-called sunshine vitamin whose deficits are increasingly blamed for everything from cancer and heart disease to diabetes; vitamin d deficiency is a serious health concern that could be affecting your health; Many people use vitamin d cream for alopecia and to greatly strengthen their immune systems to fight off colds, sickness, and disea
Prices pulled from the Amazon Product Advertising API on:
Product prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.
It is important to note that none of these methods will give you the same deep, dark tan that you can get from natural tanning. However, they can help to create a healthy, natural-looking glow without the risks associated with natural tanning.
Tips about self-tanner and tanning products are given in the FAQ section.
Why “without exposing your skin to sun rays”? Isn’t exposure to the sun good i.e. natural tan?

The term “natural tanning” is often used interchangeably with “exposure to sun rays,” but they are not quite the same thing. Natural tanning is the process of your skin darkening in response to exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or from artificial sources, such as tanning beds. The UV radiation triggers your body to produce more melanin, the pigment that gives your skin its color. The more melanin you have, the darker your skin will be.
As discussed earlier exposure to sun rays can be harmful to your skin because UV radiation can damage the DNA in your skin cells. This damage can lead to skin cancer, premature aging, and other health problems.
So, while natural tanning is a natural process, it is not without risks. If you want to get a tan, it is important to do so safely. You can do this by using self-tanners, bronzers, or tanning drops just discussed above. These products will give you a tan without exposing your skin to harmful UV rays.
So natural tan is not beneficial i.e. tanning bed and UV rays of the sun?
There is no scientific evidence to support the claim that natural tanning is beneficial. The American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) states that “there is no safe way to tan.” The AAD also states that “tanning, whether from the sun or a tanning bed, increases your risk of skin cancer.”
The AAD recommends that people avoid tanning altogether and instead protect their skin from the sun’s harmful UV rays by wearing sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher, seeking shade during the middle of the day, and wearing protective clothing.
While some people believe that natural tanning can help to protect the skin from the sun’s harmful rays, this is not the case. Tanning makes the skin more susceptible to damage from UV rays. This is because tanning is a sign that the skin has been damaged by UV rays.
Still, if someone wants to bask or sit in the sun for tanning, what is the best time and how much should they sit?

The best time to tan is early in the morning or late in the afternoon when the sun’s rays are not as strong. You should also avoid tanning during the middle of the day when the sun’s rays are strongest.
It’s also important to start slowly and gradually increase the amount of time you spend in the sun. This will help your skin adapt to the sun’s rays and minimize the risk of sunburn.
As a general rule, you should never tan for more than 20 minutes at a time. And be sure to apply sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher every two hours, even if you’re tanning.
By following these tips, you can safely tan without damaging your skin.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, tanning is a natural process that occurs when the skin is exposed to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or artificial sources. However, there is a limit to how much melanin your body can produce, so your skin will eventually stop tanning at a certain point. The exact point at which this happens will vary depending on various factors, such as your skin type, age, and sun exposure.
While some people believe that natural tanning is beneficial, there is no scientific evidence to support this claim. In fact, tanning, whether from the sun or a tanning bed, increases your risk of skin cancer, premature aging, and other health problems.
If you want to get a tan, it is important to do so safely. You can do this by using self-tanners, bronzers, or tanning drops. These products will give you a tan without exposing your skin to harmful UV rays.
It is also important to protect your skin from the sun’s harmful UV rays by wearing sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher, seeking shade during the middle of the day, and wearing protective clothing.
By following these tips, you can get a tan safely and protect your skin from the sun’s harmful rays.
FAQ
Q: What is the difference between tanning and sunbathing?
A: Tanning is the process of your skin darkening in response to exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or from artificial sources. Sunbathing is the act of exposing your skin to the sun’s rays for the purpose of tanning.
Q: What is the difference between natural tanning and artificial tanning?
A: Natural tanning is the process of your skin darkening in response to exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or from artificial sources. Artificial tanning is the use of tanning beds or other devices to expose your skin to UV radiation.
Q: What are the different types of self-tanners?
A: There are two main types of self-tanners: lotions and mousses. Lotions are the most common type of self-tanner. They are easy to apply and blend well. Mousses are a newer type of self-tanner. They are more difficult to apply than lotions, but they give a more natural-looking tan.
Q: How long does a self-tanner last?
A: A self-tanner will last for about 7-10 days. The exact amount of time will vary depending on the type of self-tanner you use and your skin type.
Q: How can I avoid getting streaks when using self-tanner?
A: Here are some tips for avoiding streaks when using self-tanner:
- Exfoliate your skin before applying self-tanner. This will help to remove dead skin cells and give the self-tanner a more even application.
- Apply self-tanner in thin, even layers. This will help to prevent streaks from forming.
- Start at your feet and work your way up to your face. This will help to prevent the self-tanner from pooling in your hands or feet.
- Apply self-tanner to your hands and feet last. This will help to prevent them from looking darker than the rest of your body.
- Let the self-tanner dry completely before getting dressed.
Q: What are some tips for applying bronzer?
A: Here are some tips for applying bronzer:
- Start with a light application of bronzer. You can always add more bronzer later, but it is difficult to remove.
- Apply bronzer to the areas of your face that you want to highlight, such as your cheekbones, temples, and jawline.
- Blend the bronzer well so that it does not look obvious.
- You can also use bronzer to contour your face. To do this, apply bronzer to the areas of your face that you want to make look smaller, such as your nose and chin.








