Diabetes is a serious condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is caused by high blood sugar levels, which can damage the blood vessels and lead to poor circulation especially affecting the extremities of the body i.e. feet. Poor circulation can also cause a variety of problems, including pain, numbness, and sores. In severe cases, it can lead to amputation.
In this article, we will discuss why diabetics are more likely to have poor circulation, the symptoms of poor circulation, and how to improve circulation.
What is diabetes?
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN DIABETES MELLITUS AND DIABETES INSIPIDUS

Diabetes is a chronic health condition that affects how your body turns food into energy. When you have diabetes, your body either doesn’t make enough insulin or can’t use the insulin it makes as well as it should. Insulin is a hormone that helps your body use glucose for energy. Glucose is a type of sugar found in the blood.
If you don’t have enough insulin or your body can’t use insulin, glucose builds up in your blood. This can lead to serious health problems, such as heart disease, stroke, blindness, kidney disease, and nerve damage.
There is no cure for diabetes, but it can be managed with medication, diet, and exercise. With proper management, people with diabetes can live long and healthy lives.
There are two main types of diabetes: type 1 and type 2.
Sure, here is a definition of diabetes type 1 in 2-3 lines, with each line in a separate heading:
Type 1 Diabetes:

Type 1 diabetes is the type of diabetes where the body cannot produce insulin at all. This is because the body’s immune system attacks the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin. People with type 1 diabetes must take insulin injections every day to manage their blood sugar levels.
Type 2 diabetes:
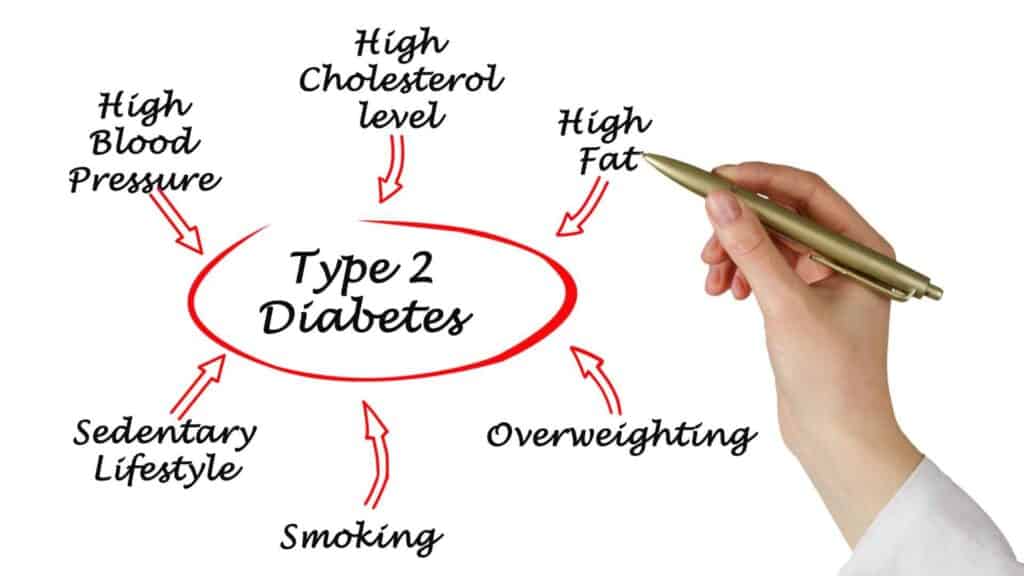
Type 2 diabetes is the type of diabetes where the body does not produce enough insulin or does not use insulin effectively. This is often due to obesity, lack of exercise, and certain medications. People with type 2 diabetes can often manage their blood sugar levels with diet, exercise, and medication. However, some people with type 2 diabetes may eventually need to take insulin injections.
Here is a table that summarizes the differences between type 1 and type 2 diabetes:
| Feature | Type 1 Diabetes | Type 2 Diabetes |
| Cause | Autoimmune attack on pancreas cells | Insulin resistance |
| Symptoms | Frequent urination, excessive thirst, unexplained weight loss, blurry vision | Fatigue, frequent urination, unexplained weight loss, slow-healing sores |
| Treatment | Insulin injections | Diet, exercise, medication, insulin injections (if needed) |
What is poor circulation?
Poor circulation is a condition in which blood flow to the body’s extremities is reduced. This can cause a variety of problems, including pain, numbness, and sores.
Why are diabetics more likely to have poor circulation?
Diabetics are more likely to have poor circulation because high blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels. High blood sugar levels can also lead to inflammation, which can further damage the blood vessels.
How does high blood sugar damage blood vessels?
- High blood sugar levels can damage the lining of blood vessels.
- This can lead to inflammation and the formation of plaque.
- Plaque can narrow the blood vessels and reduce blood flow.
Other factors that contribute to poor circulation in diabetics.
- Smoking:

Smoking damages the blood vessels and makes them more likely to clot.
- High cholesterol:
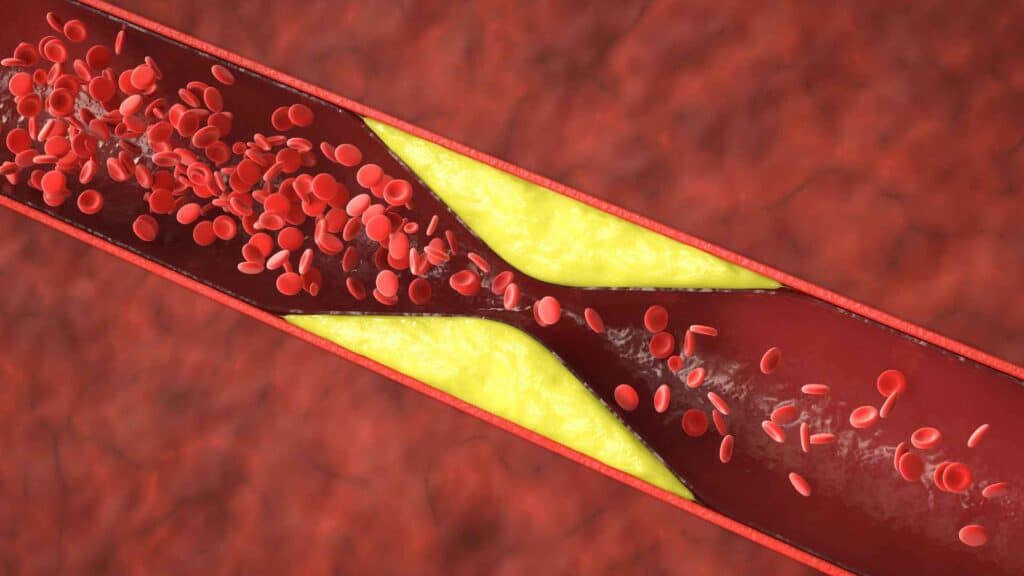
High cholesterol levels can build up in the blood vessels and narrow them.
- High blood pressure:
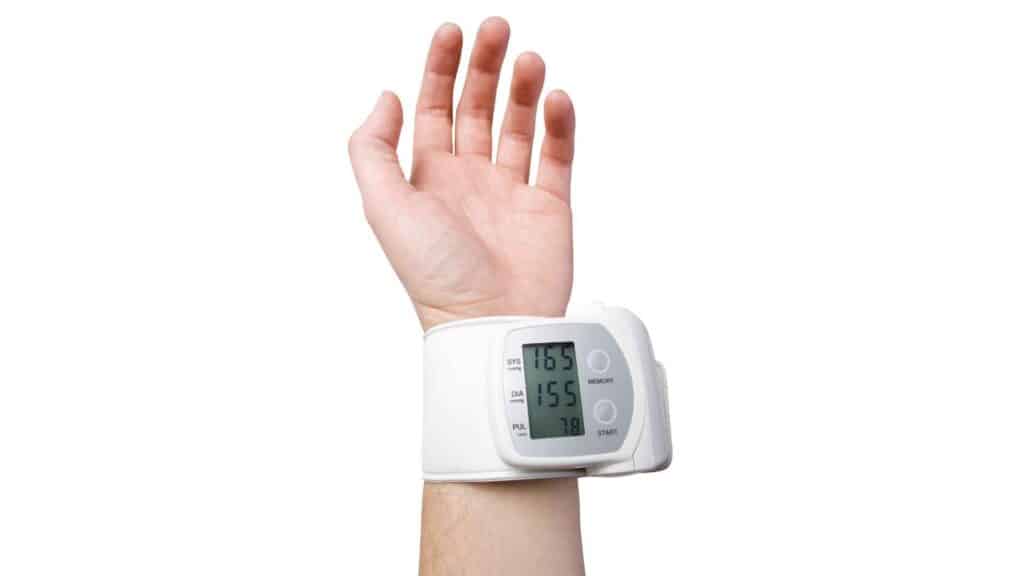
High blood pressure can damage the blood vessels and make them more likely to narrow.
- Obesity:

Obesity is a major risk factor for poor circulation.
- Age:

As people age, their blood vessels become more susceptible to damage.
- Family history:

People with a family history of poor circulation are more likely to develop the condition themselves.
Symptoms of poor circulation
Following are some of the symptoms in diabetics and also in non-diabetics.
- Pain, numbness, or tingling in the hands and feet:
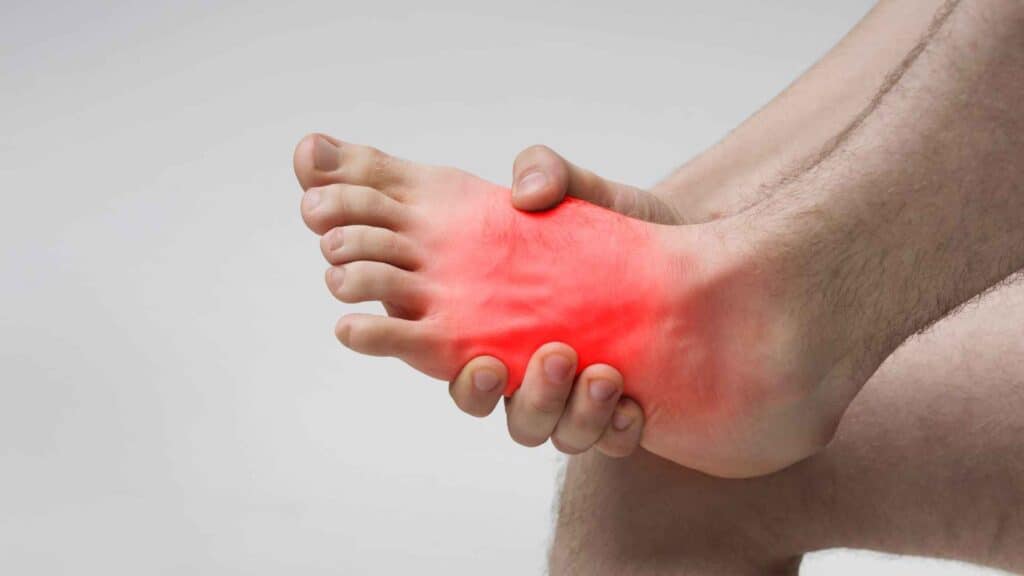
As discussed earlier diabetics have high blood glucose levels. This can damage the blood vessels, which can reduce blood flow to the extremities. When blood flow is reduced, it can cause pain, numbness, or tingling in the hands and feet.
- Cold hands and feet:

Cold hands and feet are common symptoms of poor circulation in diabetics. When blood flow to the extremities is reduced, it can cause the hands and feet to feel cold but they can also be caused by other things in non-diabetics, such as:
- Exposure to cold weather

When the weather is cold, the body’s natural response is to constrict the blood vessels in the extremities to conserve heat. This can also lead to cold hands and feet.
- Sitting or standing for long periods of time

When you sit or stand for long periods, the blood flow to your extremities can be reduced. This can also lead to cold hands and feet.
- Certain medications
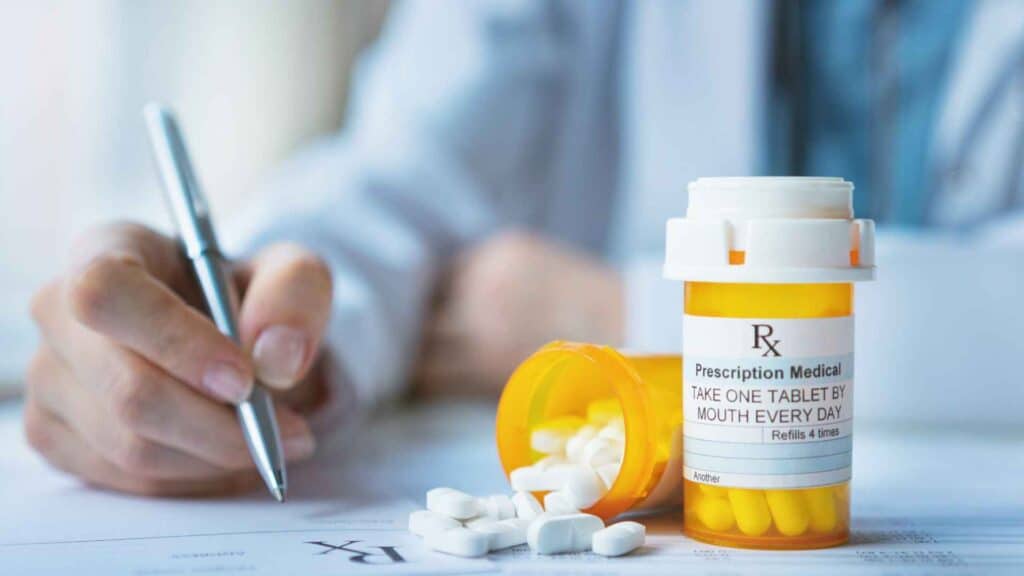
Some medications, such as beta-blockers, can cause cold hands and feet as a side effect.
- An underlying medical condition
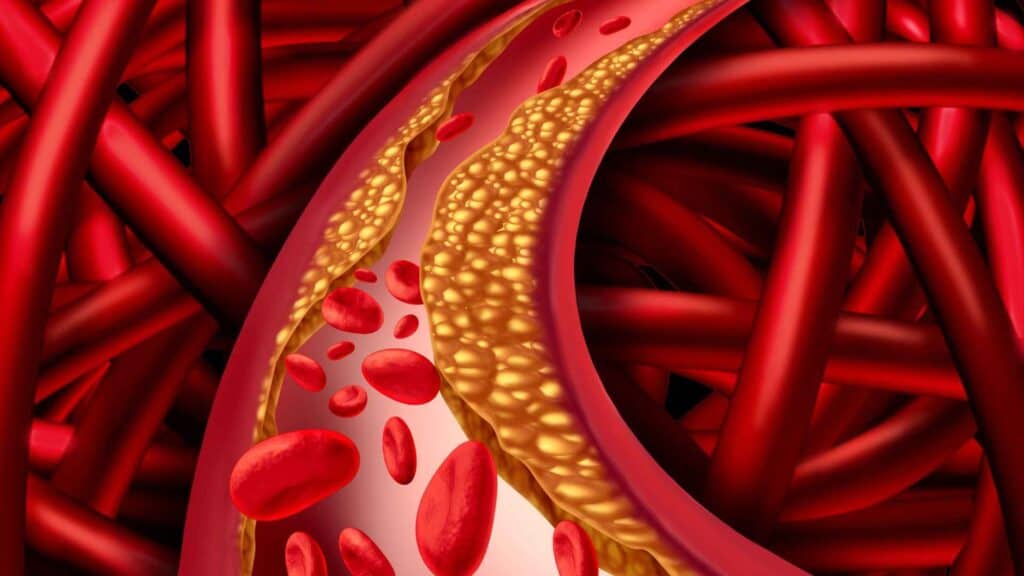
Cold hands and feet can also be a sign of an underlying medical condition, such as Raynaud’s phenomenon, or peripheral artery disease.
- Slow-healing sores
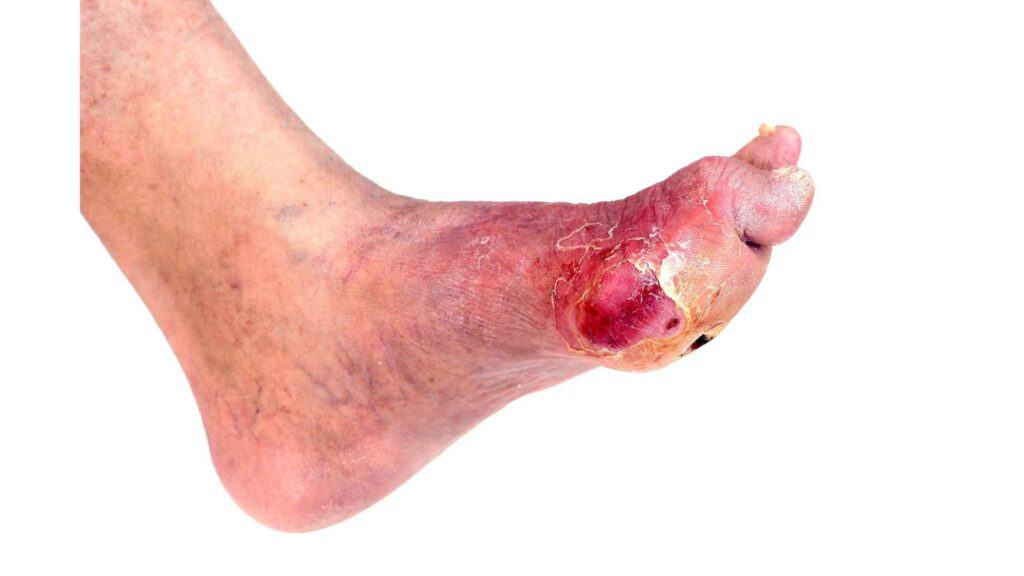
Slow-healing sores, or diabetic ulcers, are a common complication of diabetes. They occur when the blood supply to the skin is reduced. This can lead to sores that take weeks or even months to heal. Diabetic ulcers can occur anywhere on the body, but they are most common on the feet. There are a number of things that diabetics can do to prevent and treat diabetic ulcers, such as controlling blood sugar levels, checking their feet daily, and taking good care of their feet.
- Changes in skin color
Changes in skin color, such as darkening or lightening of the skin, can be a sign of diabetes. These changes are caused by damage to the blood vessels in the skin. The most common areas affected are the neck, armpits, and groin. Changes in skin color can be a sign of prediabetes or type 2 diabetes. If you notice any changes in your skin color, it is important to see a doctor to get tested for diabetes.
Here are some of the changes in skin color that can be caused by diabetes:
Acanthosis nigricans:
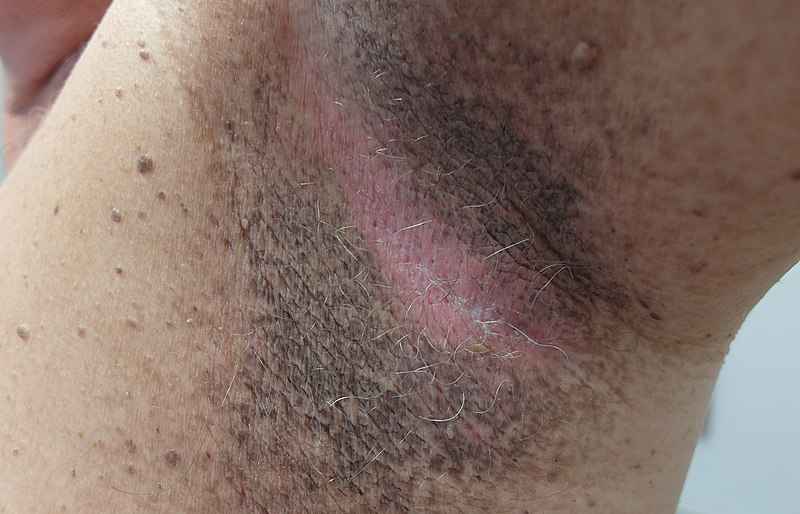
This is a condition that causes dark, velvety patches of skin to appear in the folds of the skin, such as the neck, armpits, and groin.
Necrobiosis lipoidica diabeticorum:
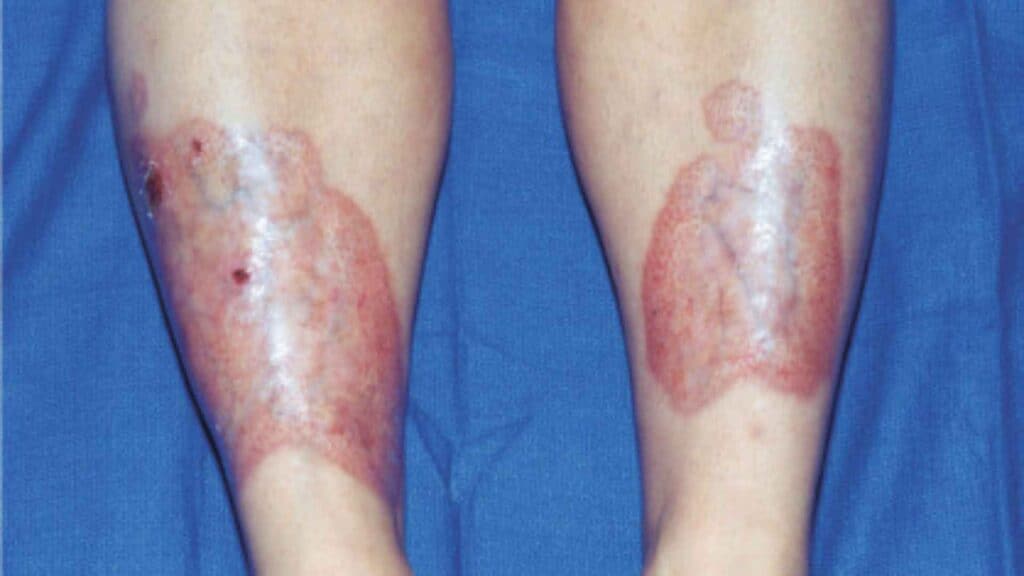
This is a condition that causes yellow, waxy patches of skin to appear on the legs.
Diabetic dermopathy:
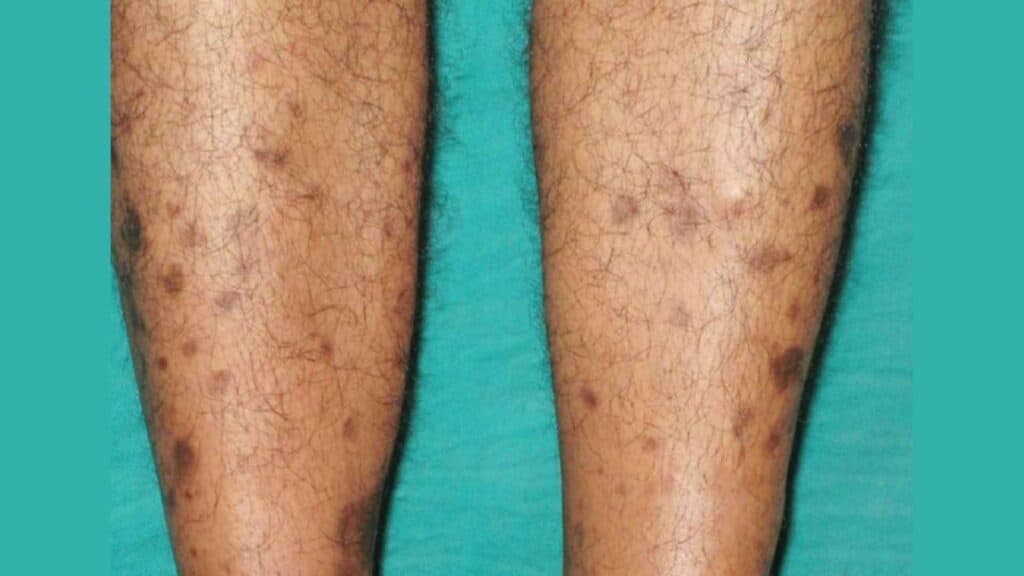
This is a condition that causes small, brown spots to appear on the shins.
These changes in skin color are not harmful, but they can be a sign of diabetes. If you notice any changes in your skin color, it is important to see a doctor to get tested for diabetes.
Thickening of the toenails
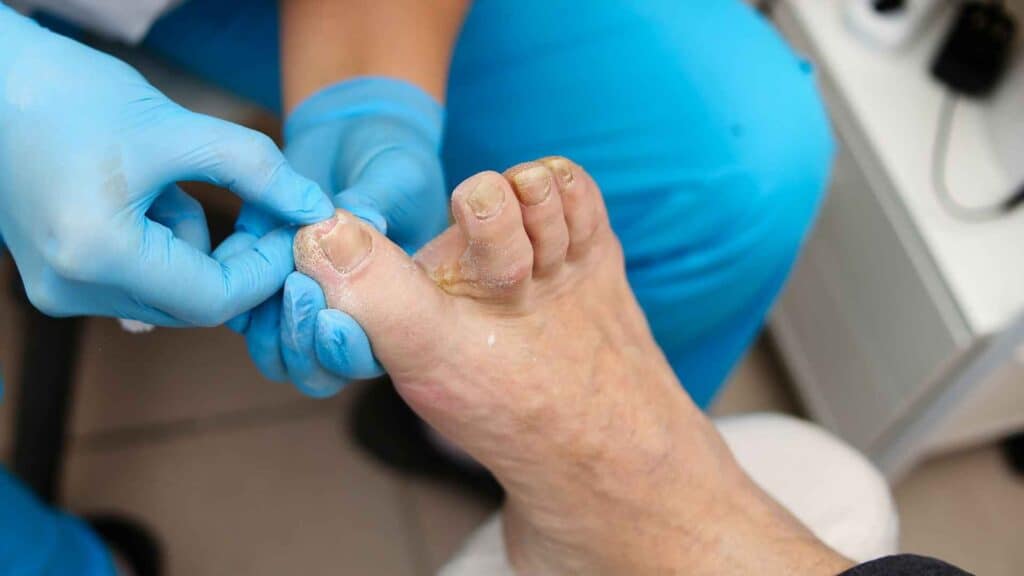
High blood glucose levels can cause thickened toenails in a number of ways.
First, high blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels in the feet. This can lead to poor circulation, which can make it difficult for the body to deliver oxygen and nutrients to the toenails. As a result, the toenails may become thick, brittle, and discolored.
Second, high blood sugar levels can promote the growth of fungi. Fungi are microscopic organisms that can live on the skin and nails. When fungi grow out of control, they can cause an infection. This infection can cause the toenails to become thick, discolored, and painful.
Third, high blood sugar levels can weaken the nails. This can make them more likely to break, split, or thicken.
If you have diabetes and you notice that your toenails are becoming thick, brittle, or discolored, it is important to see a doctor. The doctor can rule out any underlying medical conditions and recommend treatment options.
- Swelling in the legs and feet
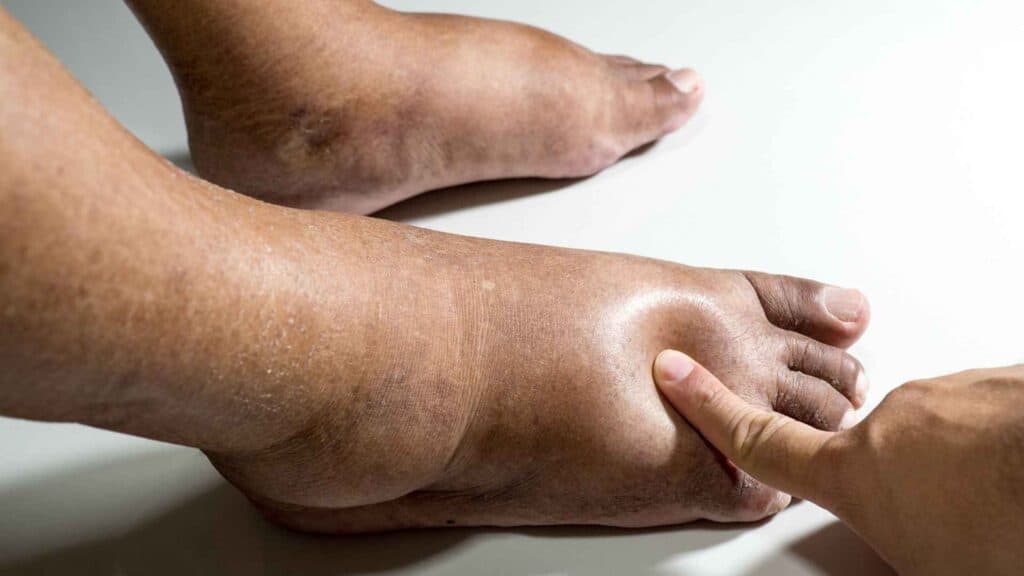
Swelling in the legs and feet, also known as edema, is a common symptom of diabetes. It is caused by a buildup of fluid in the tissues. This can happen for a number of reasons, including:
- Poor circulation:
Diabetes can damage the blood vessels, which can lead to poor circulation. This can make it difficult for the blood to return to the heart, which can cause fluid to build up in the tissues.
- Kidney disease:
Diabetes can damage the kidneys, which can lead to kidney disease. Kidney disease can cause the body to retain fluids, which can lead to swelling.
- Heart disease:
Diabetes can increase the risk of heart disease. Heart disease can cause the heart to not pump blood as effectively, which can lead to fluid buildup.
- Pregnancy:
Swelling in the legs and feet is a common symptom of pregnancy. This is because the body produces more fluids during pregnancy, which can lead to fluid buildup.
Swelling in the legs and feet can be mild or severe. It can be temporary or long-term. In some cases, swelling can be a sign of a serious medical condition. If you have swelling in your legs and feet, it is important to see a doctor to rule out any underlying medical conditions.
Fatigue

Fatigue is a common symptom of diabetes. Beside diabetes it is caused by a number of factors, including:
- High blood sugar levels:
High blood sugar levels can damage the nerves and blood vessels, which can lead to fatigue.
- Anemia:
Anemia is a condition in which the body does not have enough red blood cells. Red blood cells carry oxygen to the body’s tissues, and when there are not enough red blood cells, the tissues do not get enough oxygen. This can lead to fatigue.
- Depression:
Depression is a common mental health condition that can cause fatigue.
- Other medical conditions:
Fatigue can also be caused by other medical conditions, such as heart disease, kidney disease, and thyroid problems.
Fatigue can be mild or severe. It can be temporary or long-term. In some cases, fatigue can interfere with a person’s daily life.
Shortness of breath

Shortness of breath, also known as dyspnea, is a common symptom of diabetes. It is caused by a number of factors, including:
- High blood sugar levels:
High blood sugar levels can damage the heart and lungs, which can lead to shortness of breath.
- Heart disease:
Diabetes can increase the risk of heart disease. Heart disease can make it difficult for the heart to pump blood, which can lead to shortness of breath.
- Lung disease:
Diabetes can increase the risk of lung diseases, such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Lung diseases can make it difficult to breathe, which can lead to shortness of breath.
- Weight gain:
People with diabetes are more likely to be overweight or obese. Weight gain can put pressure on the lungs, which can lead to shortness of breath.
These are some of the symptoms of diabetes. All symptoms come to one point i.e. high blood glucose level. How to control it, stay tuned, this will be discussed in the upcoming “How to Improve Circulation” section.
Complications of poor circulation
Now we will discuss the complication produced due to poor circulation in diabetes but it can also be caused in non-diabetics if poor circulation is their problem.
- Heart disease:
Heart disease is the leading cause of death for people with diabetes.
- Stroke:
Stroke is the fifth leading cause of death for people with diabetes.
- Peripheral artery disease (PAD):
PAD is a narrowing of the arteries in the legs that can lead to pain, numbness, and sores.
- Gangrene:
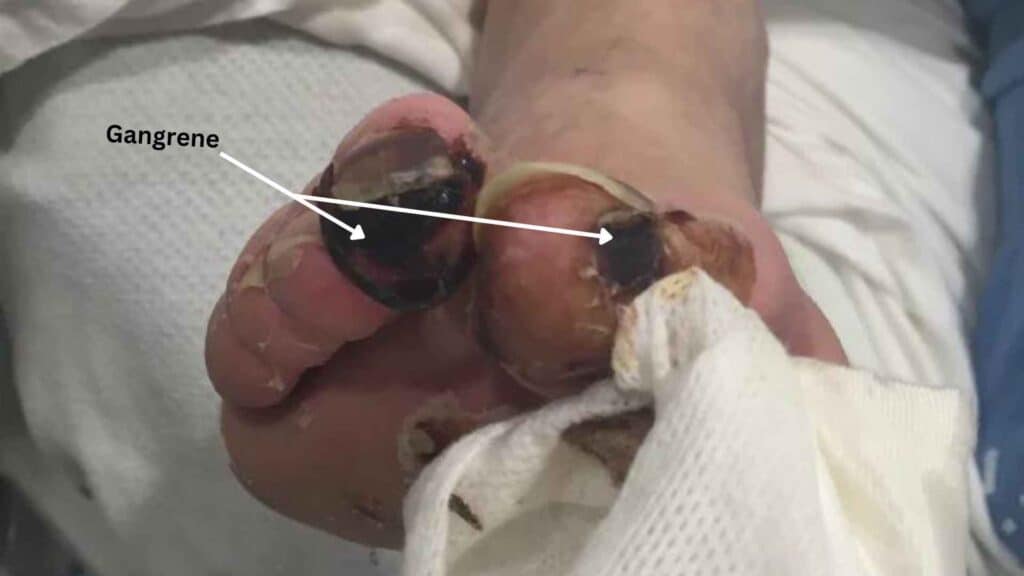
Gangrene is a tissue death that can occur in the extremities due to poor circulation. It may also occur due to circulation obstruction and bacterial infection.
- Vision loss:
Diabetes can damage the blood vessels in the eyes, leading to vision loss.
- Kidney disease:
Diabetes can damage the kidneys, leading to kidney failure.
- Nerve damage:
Diabetes can damage the nerves, leading to numbness, tingling, and pain.
- Sexual dysfunction:
Diabetes can damage the nerves and blood vessels in the genitals, leading to sexual dysfunction.
How to improve circulation
Following are some of the suggestions to improve poor circulation in diabetics and also in non-diabetics.
- Control blood sugar levels:
This is the most important thing that diabetics can do to improve their circulation. By keeping their blood sugar levels under control, diabetics can reduce the damage to their blood vessels.
- Quit smoking:
Smoking damages the blood vessels and makes them more likely to clot. Quitting smoking can help to improve circulation.
- Exercise regularly:
Exercise helps to improve circulation by increasing blood flow. Diabetics should aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
- Eat a healthy diet:
A healthy diet includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. These foods are low in saturated fat and cholesterol, and they help to keep blood sugar levels under control.
- Maintain a healthy weight:
Obesity is a major risk factor for poor circulation. By maintaining a healthy weight, diabetics can reduce their risk of developing this condition.
- Control your blood pressure:
High blood pressure can damage blood vessels and make it harder for blood to flow. If you have high blood pressure, work with your doctor to get it under control.
- Get enough sleep:
Sleep is important for overall health, including circulation. Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep each night.
- Manage stress
Stress can raise blood sugar levels, which can damage blood vessels and make it harder for blood to flow. Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as exercise, yoga, or meditation.
- Wear comfortable shoes that fit well
Avoid wearing shoes that are too tight or too loose.
- Take medication:
In some cases, doctors may prescribe medication to help improve circulation.
- See a doctor regularly:
Diabetics need to see their doctor regularly to monitor their blood sugar levels and to look for any signs of complications.
Conclusion
So, in conclusion, we concluded that the answer to the question “Why do diabetics have poor circulation” is that diabetics have high glucose buildup in the extremities, which slows down the blood flow to these areas. This can lead to a number of complications, such as:
- Peripheral artery disease (PAD):
PAD is a condition that occurs when the arteries in the legs become narrowed or blocked, which can reduce blood flow to the legs. PAD can cause pain, cramping, and numbness in the legs, and it can also increase the risk of amputation.
- Foot ulcers:
Foot ulcers are open sores that can develop on the feet of diabetics. Foot ulcers can be caused by a number of factors, including poor circulation, high blood sugar levels, and nerve damage. Foot ulcers can be serious, and they can sometimes lead to amputation.
- Heart disease:
Diabetics are at an increased risk of developing heart disease. Heart disease is a condition that affects the heart and blood vessels. It can cause chest pain, shortness of breath, and heart attack.
- Stroke:
A stroke is a sudden loss of blood flow to the brain. It can cause paralysis, speech problems, and other neurological problems.
How to control it?
There are a number of things that diabetics can do to reduce their risk of developing poor circulation and its complications. These include:
- Controlling their blood sugar levels:
This is the most important thing that diabetics can do to improve their circulation. By keeping their blood sugar levels in a healthy range, they can help to prevent further damage to their blood vessels.
- Quitting smoking:
Smoking damages the blood vessels and makes it harder for blood to flow. Quitting smoking is one of the best things that diabetics can do for their overall health, including their circulation.
- Exercising regularly:
Exercise helps to improve circulation by keeping the blood vessels healthy and by increasing the heart’s ability to pump blood. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
- Eating a healthy diet:
A healthy diet is important for overall health, including circulation. Make sure to eat plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Maintaining a healthy weight:
Excess weight can put a strain on the heart and blood vessels, making it harder for blood to flow. If you are overweight or obese, losing even a small amount of weight can help improve circulation.
- Taking medication, if needed:
If you have diabetes, your doctor may prescribe medication to help control your blood sugar levels and improve your circulation.
By following these tips, diabetics can help to improve their circulation and reduce their risk of developing serious complications.





