Outline
What is glucose? (See the conversation.)
What are hormones?
What is insulin?
What is Glucagon?
How do they work?
Diabetes and its types.
Symptoms.
Glucose monitor system and their types.
- Self-monitoring glucose system
- Continuous glucose monitoring system
Their pros and cons.
Their apparatus.
Tips before pricking a finger.
Conclusion (which one is best).
Are you searching for the best glucose monitor system for diabetes?
Of course, that’s why we are here.
Okay but wait please,
Do you know what is glucose, how it works, and what are the effects due to an increase and decrease in glucose concentration?
All right, these terms are most important for you to know about it before selecting the best glucose monitor system because generally these terms are mentioned for selecting.
Okay, let’s start with the first question
what is glucose?

In simple words that are easy for everyone
“Glucose is a simple sugar with molecular formula C6H12O6. “
Simple sugar means the simplest form of carbohydrates and carbohydrates are the compounds of carbon and hydrogen or in other words, compounds derived from living organisms are called carbohydrates.
Still confused, don’t worry let me assume you a daily life example.
Ohh, that’s interesting!

Yes, man, I am here to make it very clear.
When you are going to work in the morning, you are fresh and vigor but after continuous work from morning to noon or taking 2, or 3 classes you become tired, and feel fatigued.
That’s correct.
So then what do you do after getting to this situation?

Well, looking at the clock when will the tik of clock hit lunchtime.
Then after that?

Eat some food and drinks and after that, we get refreshed.
Yes, that’s the point, the refreshing is basically the glucose that makes you like this, in short glucose is the fuel and energy to the body.
How does glucose work and how it is controlled in our bodies?
Did you hear about the words Insulin and Glucagon, I think most of you are aware of this, but if not so let me explain to you.
These are called hormones.
Hormones?
What are hormones?
Well, hormones are secreted by glands that are
“Secretions of special cells (glands) in our body which is transported in the blood (endocrine glands) or through the special duct (exocrine glands) to the target area where cells and tissues are activated for required action.”
So you are clear about hormones,
Now, how do insulin and glucagon hormones work to control glucose levels normally?
Before discussing these hormones, keep in mind that these two hormones are antagonistic i.e opposite in their work.
How?
Let’s go back to the example I gave you earlier when you were active and vigorous in the morning because your blood has an excess of glucose. Some of them are used for your activities until you feel exhausted and need energy. And the excess glucose is stored in an organ called the liver and muscle cells.
But here we didn’t hear about insulin and glucagon?
Be calm, I was just talking about that.
As I said excess glucose is stored in the liver and muscle cells.
Really.

Yes, that was insulin hormone which was secreted by an organ called the pancreas into the blood and reaches the liver where the permeability of liver cells is increased and the excess glucose is stored but in another form called glycogen in the liver.
What is glycogen?
Well, glycogen is a multi-branched polysaccharide.
(Poly means many and saccharide means sugar i.e glucose) it is reserved food for animals and humans.
That’s good.
Hold on it’s not the end.
Did you forget glucagon?
Ohh, sorry.
Glucagon is a hormone that is secreted by the pancreas too.
When it is secreted?
When there is a need for glucose in the body, just as you are working the whole day and when you are not eating or taking any drink or not in the position of eating then glucose needs to be used, for this purpose, glucagon reaches the liver through the blood and converts back the glycogen to glucose.
I have confusion, both hormones are released from the pancreas?
Yes, I can understand your confusion, basically, there are three types of cells in the pancreas in the form of islets called islets of Langerhans, the name is given because of courtesy to German anatomist Paul Langerhans who discovered it. The cells are
Beta (β) cells
Alpha (α) cells and
Delta cells (we are not explaining it here, not relevant)
Beta (β) cells:
Secretes insulin.
Alpha (α) cells:
Secretes glucagon.
But who controls this check and balance and secretion process?
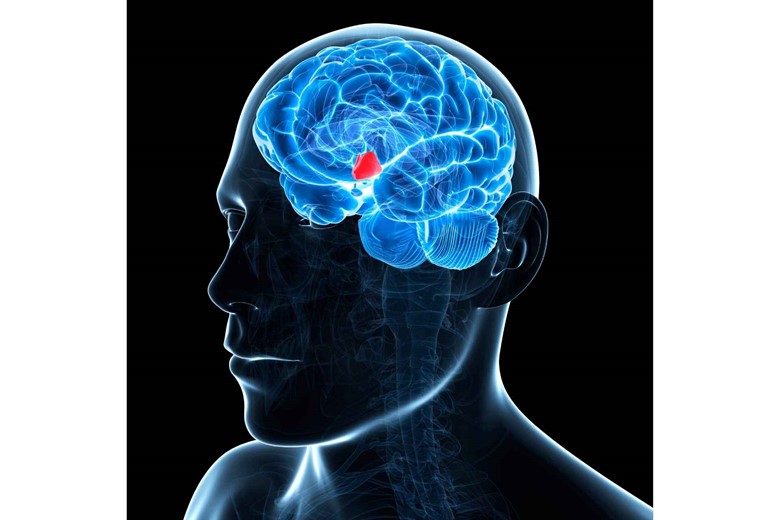
Good question, the hypothalamus of the brain control this balance. When blood passes through the hypothalamus as it is continuously passing throughout the body and if there is an increase in glucose level in the blood, the hypothalamus triggers a signal to beta (β) cells of the pancreas to secrete insulin so that the concentration comes to the normal level i.e 80 t0 120 mg/dl (milligram per deciliter).
In contrast, if the level goes down, the hypothalamus sends a signal to alpha (α) cells of the pancreas to secrete glucagon which breaks the glycogen chain to glucose from the liver and keep the body energetic.
That’s beautiful!
Now come to the abnormalities of insulin and glucagon, what are the common abnormalities related to their secretions?
This is our main concern here let’s talk about it
Abnormalities:
The most common abnormality related to insulin and glucagon is Hyposecretion and Hypersecretion.
Hypo secretion of insulin:
I am sure you are aware of hyposecretion if not then it means under secretion than a normal level. Less than 65 mg/dl (milligram per deciliter) is considered hypoglycemia. Very low about 30 mg/dl (milligram per deciliter) can lead to brain death because of getting no energy ultimately the result is death.
There must be an adverse effect on this condition, isn’t it?
Correct, the most common problem is called diabetes mellitus or simply diabetes. Diabetes insipidus is the deficiency of vasopressin which regulates kidney function, not mixed up with these terms. Diabetes is a condition where there is not enough or no insulin production to convert and store glucose to glycogen.
Before going to symptoms could you explain please the types of diabetes?
Of course, this is the most important to talk about it. They are of two types.
Diabetes mellitus type 1
Diabetes mellitus type 2
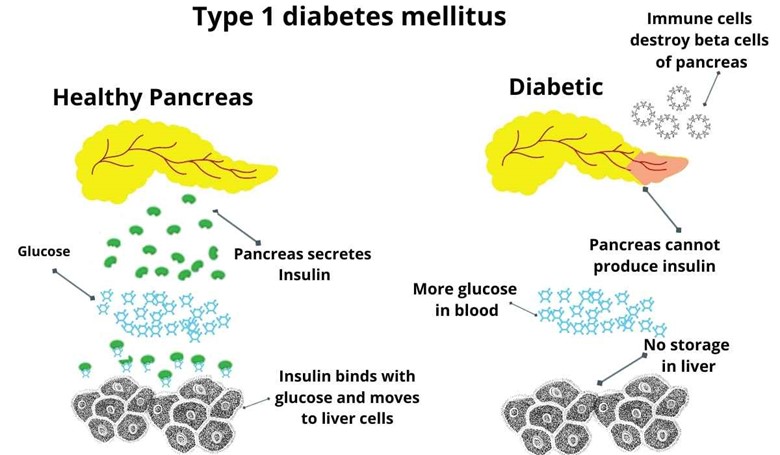
Diabetes mellitus type 1:
In diabetes mellitus type 1 the insulin is not produced by the pancreas.
Why? What is their reason?
Well, there may be possible reasons. Maybe it is
Genetic (means gene for insulin production is damaged which then cannot produce insulin)
Autoimmune (immune cells destroy beta cells of the pancreas.
What about diabetes mellitus type 2?
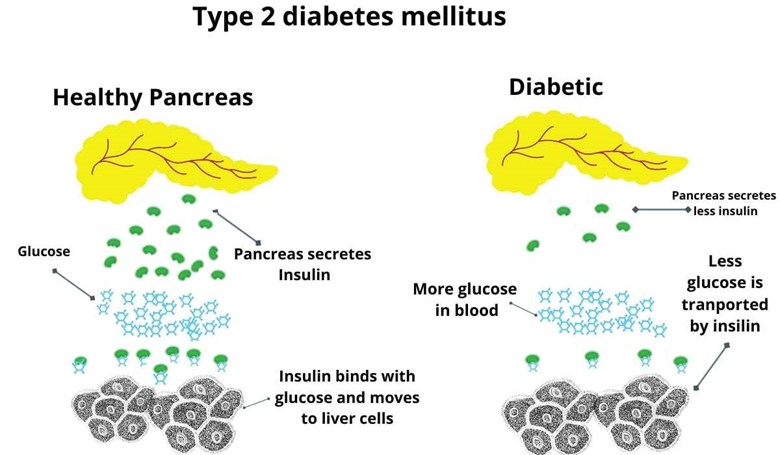
Diabetes mellitus type 2:
In type 2 insulin is produced but in a very less amount i.e. not enough for the body.
Then what happened to that glucose in the blood?
Now you are talking about symptoms.
The glucose is secreted in urine making urine yellowish color.
While other symptoms are:

- High Starvation because glucose is not stored,
- Sweating,

- Tiredness.
Now I am sure you are clear about all these, now come to monitor system.
Hypersecretion of insulin:
High glucose or sugar levels above 180 mg/dl (milligram per deciliter) can lead to classic diabetes symptoms i.e

- Loss of sensation in feet,

- Retinopathy (loss of vision)
- Loss of kidney function.
Luckily consistent high sugar levels are problematic otherwise occasionally high level is ok.
Now we are going to discuss the best glucose monitor system.
BEST GLUCOSE MONITOR SYSTEM:
Now coming to the best blood glucose monitor system for your health. Here best glucose monitor system means which one is suitable for you i.e. self-monitoring glucose system or continuous glucose monitoring system.
That’s good.
So what is a glucose monitor?

I am sure every one of you knows and experienced a journey. There is a whole system of meters in front of a driver in a vehicle.
Yes, we have watched it.

Okay, and every one of you also knows that there is a meter for fuel in the car, when the decrease in fuel occurs, the monitor makes the driver alarm that I need fuel, and of course, the driver goes to a fuel pump and refill the vehicle so to keep moving.
Did it make any sense?
Well, a little bit.
Let me explain to you, the same in the case of glucose when the glucose level is decreasing the monitor makes you alarm and you make yourself refill with glucose.
But can I ask a question, Is it necessary for everyone?

Well, Luckily normal people don’t need it but if they want to monitor then they can but again if there is an illness in non-diabetic people then it is necessary to monitor it otherwise there is no need for non-diabetic people to monitor their glucose level, however, it is very necessary for the diabetic patient because his/her glucose is not storing in the body and as mentioned earlier that low-level glucose is lethal for anyone and especially diabetic patient blood glucose or sugar level change rapidly, therefore it is very important to use glucose monitor system before it goes to the situation.
Now coming to the types of glucose monitor systems.
Which are:
1. Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose
2. A non-invasive continuous glucose meter or continuous glucose monitor
1. Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose
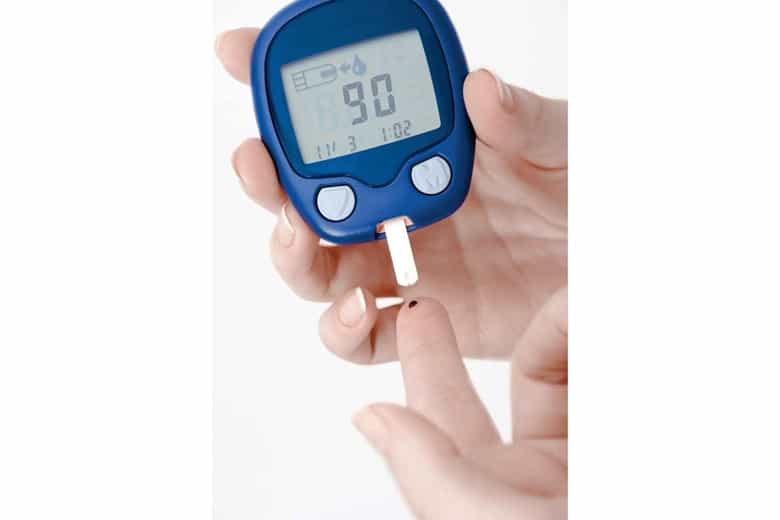
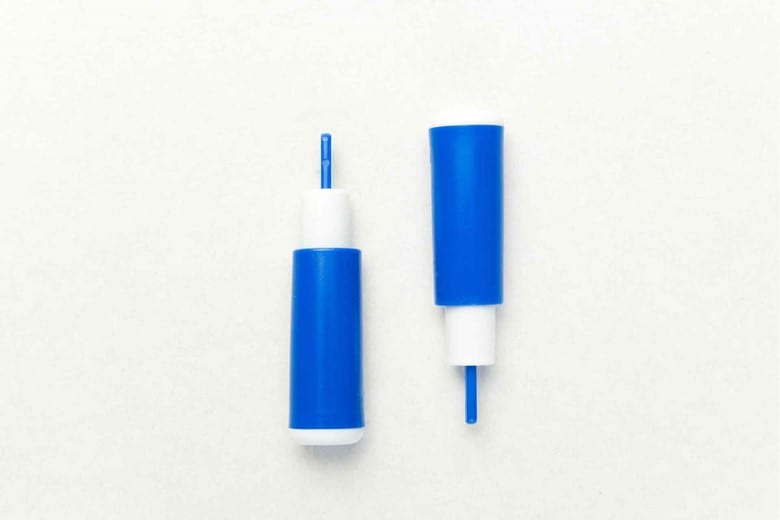
This glucose monitor system requires a minimal finger prick. Here finger pad is pricked with a lancet supplied with the meter and then blood drop is put on the strip connected to the glucose meter which gives you the results.
What apparatus is there in this blood glucose meter system?
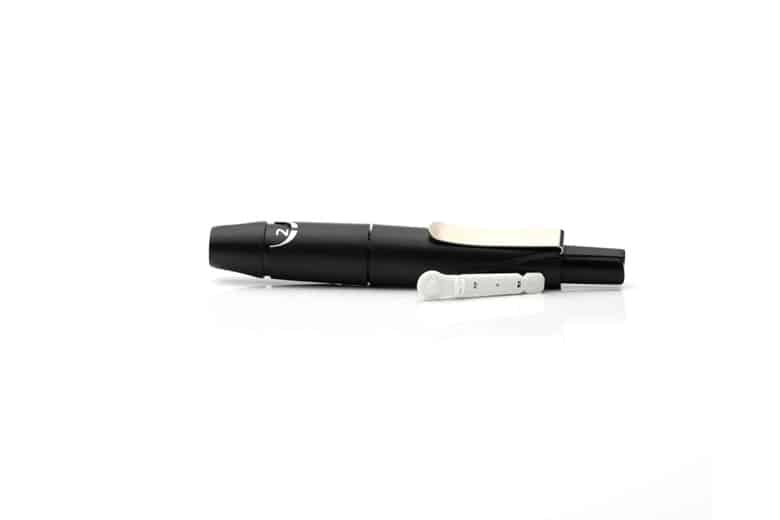

- Lancing device
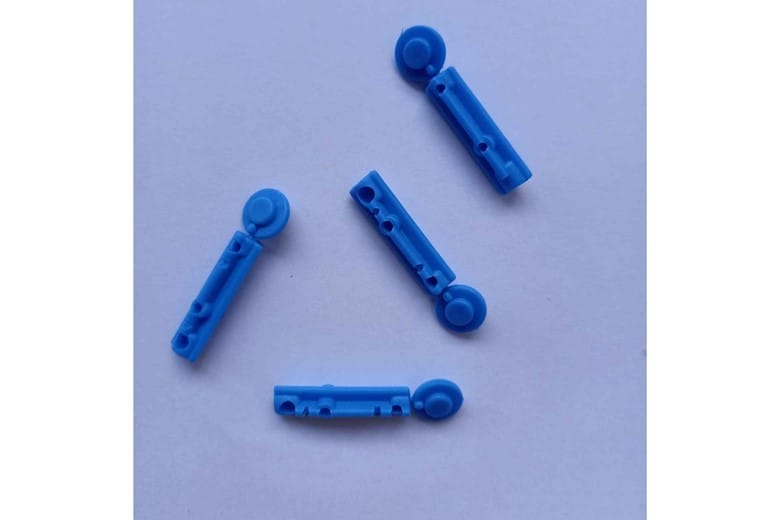

- Lancet
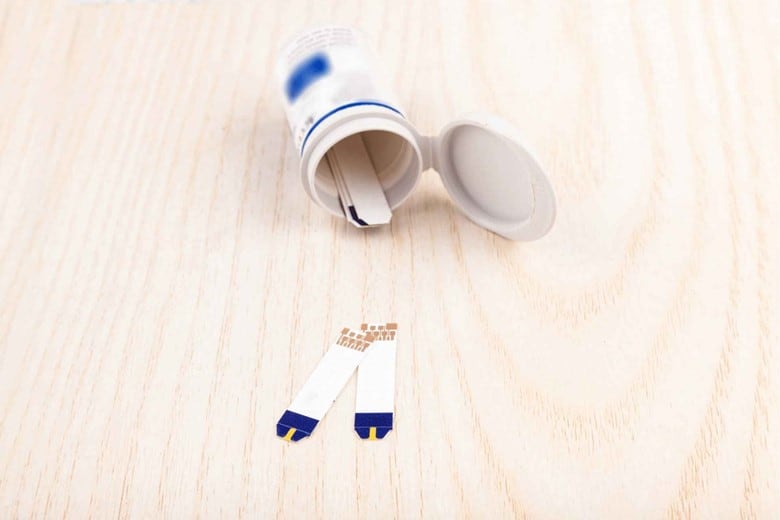

- Strip
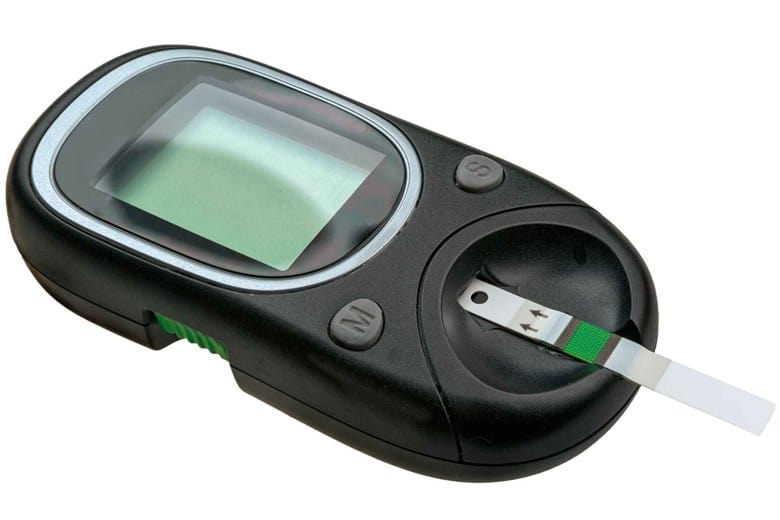

- Glucose monitor
But here I want to share some of the tips with you.
Tips before using an Invasive glucose meter:
- Use an automatic lancet device for pricking.

- Wash hands with warm water and soap and then dry. Also, rub your hands for 1 to 15 seconds because it just helps in better flow and makes it easy for collecting blood.

- Washing hands also wash sugar or sweets attached to fingers so that results don’t get wronged.

- Use a new lancet for every prick because it gets dirty and makes possible skin infections.
- Always use a control solution to check whether the glucose monitor is working properly.
- Use one kind of glucose monitor because different monitors give different slightly different values.

- Prick the sides of the finger for less pain because the finger pad (center) has more nerve endings and makes more pain.
And could you please explain how to use it?
Yes, of course, First of all, put all the kit in front of you including.
Steps:
- Then do the tips work first I.e washing hands, putting a new lancet on the lancing device, and rubbing hands.
- Put a strip in the meter and make sure it is turned on and is ready.
- Then prick the sides finger with a lancing device so that you feel less pain as the center has more nerve endings and it also has problems in fingerprint detection.
- If your hands are warmed up then you don’t need to apply pressure but if needed then gently apply pressure on the surrounding area until a drop of blood appears. Too hard squeezing is not good.
- Gently touch the drop of blood with the strip in the meter and wait for a few seconds for the results.
- Upon successful completion of the test clean any blood on the finger if any.
- Record the results and data in a monitoring diary.
- Dispose of the strip and make sure the lancet is put into the sharp bin.
Pros and cons:
| PROS | CONS |
| I. Give instant results. | i. Pain due to finger pricks. |
| ii. Accuracy is good. | ii. Pricking of the finger every time while blood checking glucose level. |
| iii. Improve control of blood glucose level. | iii. strips costly. |
| iv. Give knowledge about different sugar diets. | iv. Use of new lancet and strip every time. |
| v. Help to inform the patient and doctor whether the medication is working or not. | v. Give a snapshot just one time. |
Now can we talk about the Continuous glucose meter?
I was just heading in that direction. Let’s explain them.
2. Continuous glucose meter (CGM):
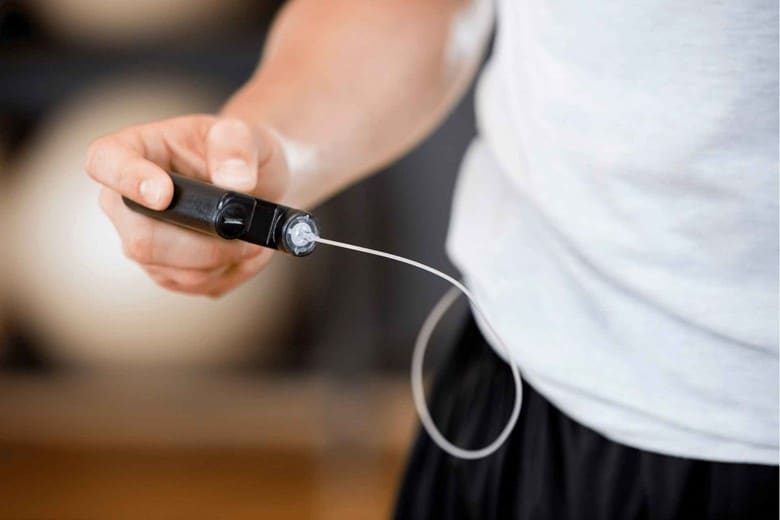

As the name shows it means continuous. Let me explain to you in simple words, it records your glucose level every after 5 minutes or some may vary in time, unlike the self-glucose monitor system which just records on the spot.
Then it means we have to keep it every time with us?
Exactly.
Ahhhhhhh…….it’s annoying.
Hold on, It’s not a ton bag, it consists of a sensor with a small transmitter that transmits data wirelessly to a receiver or a compatible phone device.
Really, so what are the items or instruments in this glucose monitor system?
The following is the list.
- Sensor
- Sensor applicator
- transmitter
How can we use it?
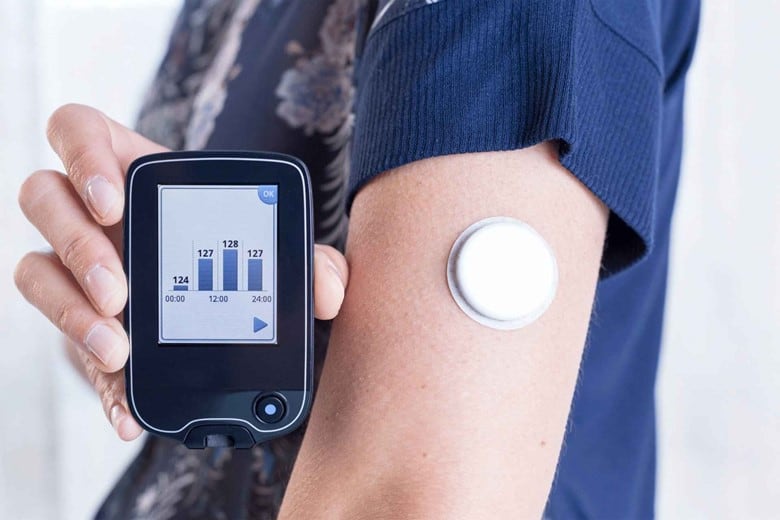
Well, it’s easy. You can fix it on the skin, on the abdomen, or arm, but I recommend the arm because during sweating the tap around the sensor may lose on the abdomen and will problems in readings.
How does it work?
Most interesting is that it needs no pricks and I am sure you are thinking now then how it measures glucose level?
Okay, keep attention, It is based on photothermal detection in which quantum light penetrates the skin where a glucose molecule absorbs it and there is a change in temperature which is detected by the sensor and gives you results of glucose level.
And how can we check the data?
Well, it is connected to a wireless receiver plus the bonus is that we can connect it to a compatible phone device too where we can receive the data.
How do we connect it to the phone?
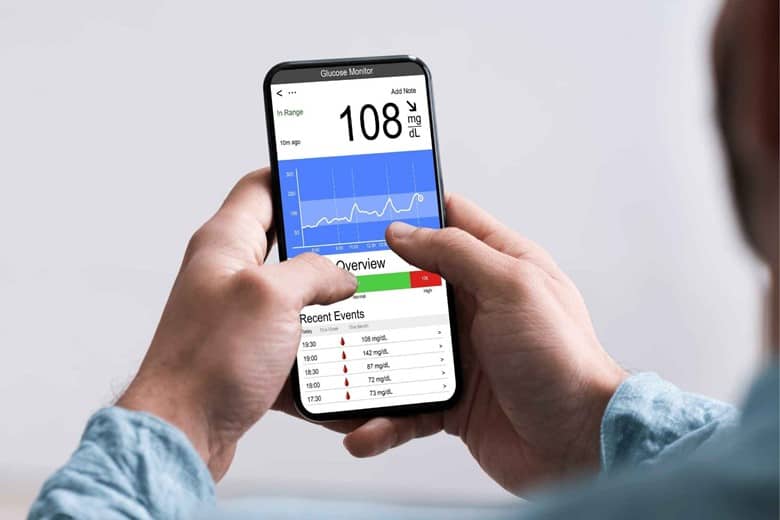

The app, a specific app allows you to connect it to your phone.
Now here I want to show high information in the following pros and cons table so that you can get a better idea.
| PROS | CONS |
| i) Show the variation in glucose level the whole day. | i) It measures blood glucose based on interstitial fluid and not the bloodstream so results may be incorrect. |
| ii) Can set alarm for a set level of glucose. | ii) You have to change the sensor which costs high. |
| iii) Alert you before the sugar level goes low below the set points on the app. | iii) Though it is small, it is attached to your body the whole time. |
| iv) Give you information on which food gives you more glucose. | iv) High price. |
| v) Help you to manage the A1c level. | |
| vi) You can gain knowledge of which activities drop sugar levels fastly. | |
| vii) Gives you more confidence and security. | |
| viii) Makes you habitual with the data so you can know the data without even looking at the results. | |
| ix) You can go for a walk and gym without fear. | |
| x) Make your alarm while sleeping at night. | |
| xi) Provide you with data with a chart. |
So which monitoring system is best for diabetic people?
Both have their own importance. The choice will be more clear in the conclusion.
CONCLUSION:
So after the whole conversation, I would recommend both the continuous glucose monitor system and the self-monitor glucose system. Now, wait, I am going to make it more clear,
If you have to check your blood sugar more than four times a day,
If you are less aware of hypo,
If you have hard physical work like gym etc,
Sportsman,
Emotional conditions i.e quick hyper conditions,
If you are a parent and want to check your child’s glucose level without going with the child,
Then I will definitely recommend you CGM, check out The best continuous glucose monitor, and if you want to go with a traditional monitoring system you can surely go with it too, check here for best Top 8 Best Self Monitoring Blood Glucose Meters or Monitors, but I recommend you both for sometimes though it is not necessary to have both but using CGM and the self-monitoring system will make you expert and will give you knowledge about glucose level in a particular time, and also you will know the particular diet for glucose if you need it and for instance, if sometimes you are out of monitoring system then you will have the idea of glucose level in that time and also let you know what kind of diet I have to take in that time. Also if you have doubts about CGM then you can check it with a self-monitoring system and can tally both.
Which one is best after use, tell me in the comment section?






1 thought on “BEST GLUCOSE MONITOR SYSTEM FOR DIABETES(A COMPLETE GUIDE)”